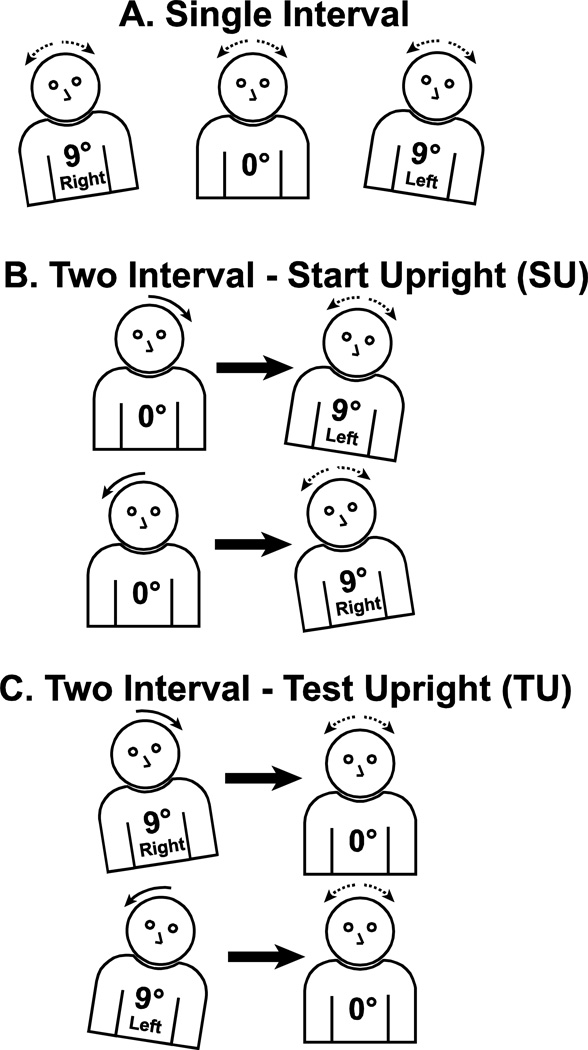
Figure 1.
Diagram demonstrating the three types of trial blocks performed in the experiment. Panel A: Single interval experiments in which starting position was fixed within the trial block, but could be upright or tilted 9° in either direction. Panel B: Two interval start upright (SU) trials. The subject began the first interval in the upright position so that after the first (adapting) stimulus they were tilted right or left. After an inter-stimulus interval (ISI) of 0.5, 3, or 6 s the test stimulus was delivered. Thus the subject was tilted at the start of the test stimulus. Each trial block included a single ISI with right and leftward rotations randomly interleaved. Panel C: Two interval test upright (TU) condition. The subject began each stimulus shifted right or left 9° so that the adapting stimulus left them upright for the start of the test stimulus. Trials with rightward and leftward rotation were randomly interleaved.