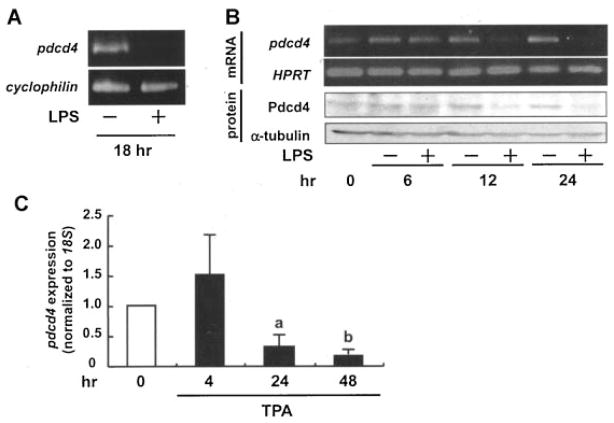
Figure 1.
Inflammatory stimuli downregulate Pdcd4 expression in macrophages. (A) Mouse peritoneal macrophages were isolated and harvested as described in the Materials and Methods Section, then exposed to LPS (500 ng/mL) for 18 h before being subjected to RT-PCR (cyclophilin used as the control). (B) RAW264.7 mouse macrophages were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 0, 6, 12, and 24 h. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to RT-PCR (hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT) was used as control) (upper panels). Alternatively, proteins were isolated and analyzed via Western blot analysis (α-tubulin served as the loading control). Images presented are representative of three independent experiments. (C) U937 human monocytic lymphoma cells were stimulated with TPA (10 nM) for 4, 24, and 48 h, total RNA was isolated and subjected to RT-qPCR (pdcd4 expression was normalized to 18S rRNA expression and given relative to control treatment). Student’s t-test was used to determine significant differences. aP <0.05 and bP <0.005 versus control.