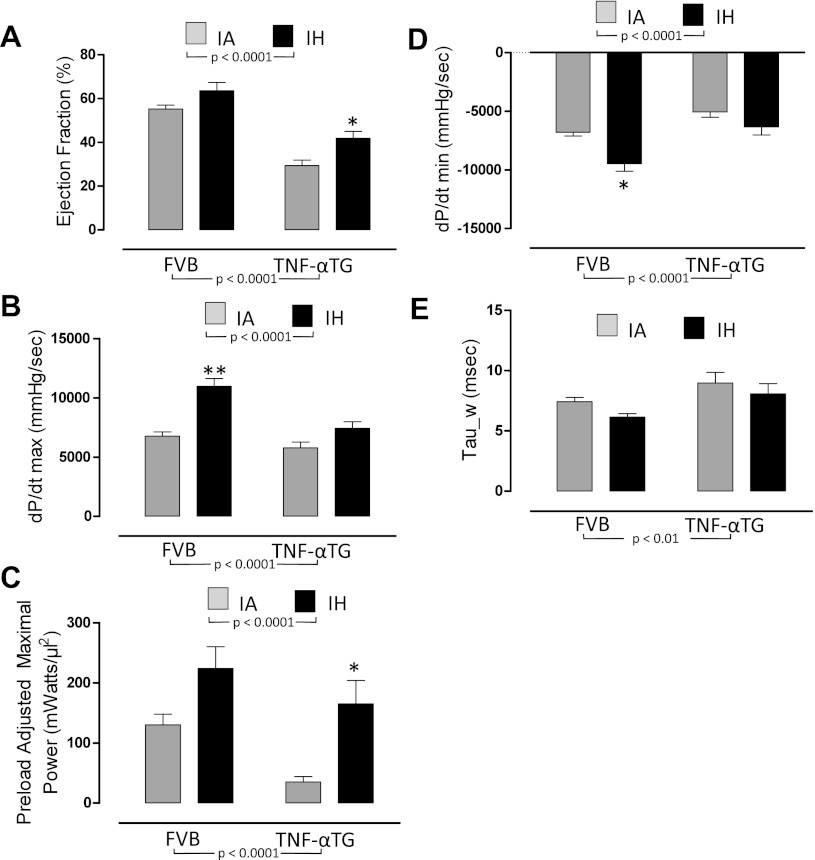
Fig. 3.
The effects of 4 wk of exposure to IA or IH on left ventricular systolic function (A–C) and diastolic function (D and E) in wild-type and TNF-αTG mice. Values are means ± SE for variables defining left ventricular systolic function [ejection fraction (A); maximum first derivative of ventricular pressure (dP/dtmax; B); preload adjusted maximal power (C)] and left ventricular diastolic function [minimum first derivative of ventricular pressure (dP/dtmin; D); relaxation constant (Tau_w; E)]. Variables were determined by steady-state pressure-volume loops in either wild-type (FVB) or TNF-α transgenic (TNF-αTG) mice after 4 wk of IH or IA exposure. Significant strain (FVB vs. TNF-αTG) effects and hypoxia (IA vs. IH) effects were determined by two-way ANOVA and are reported on the figure; there was a significant interaction for dP/dtmax only (P < 0.05). Differences between IA and IH means within each strain were determined by one-way ANOVA. **Significant difference (P < 0.01).