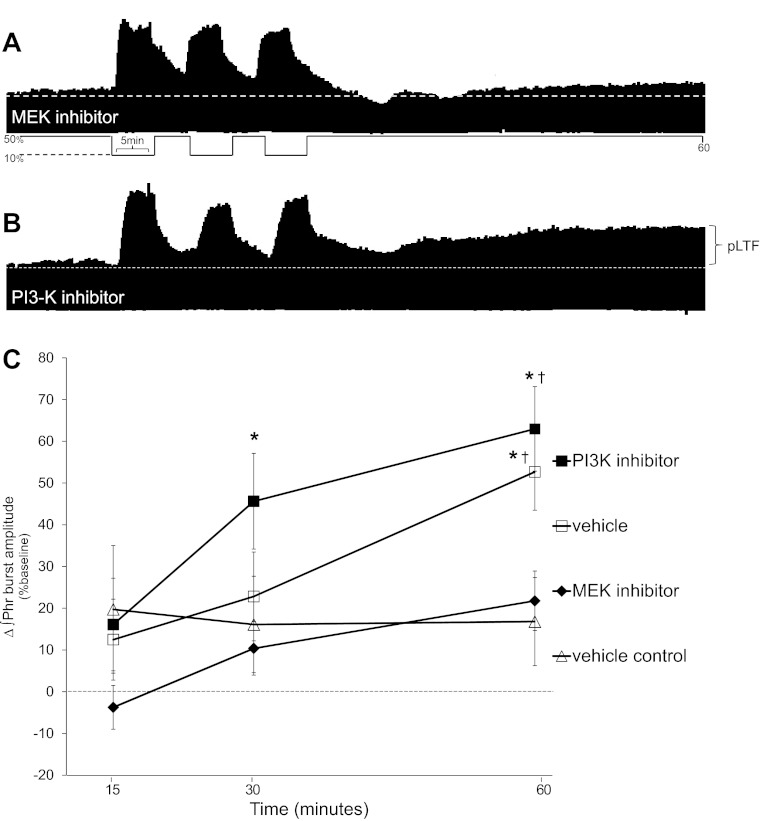
Fig. 4.
Spinal MEK inhibition blocks pLTF. A: representative phrenic neurogram after intrathecal MEK inhibitor (U0126) before AIH. B: representative phrenic neurogram after intrathecal PI3K inhibitor (PI-828) before AIH. C: comparisons were made for ∫Phr burst amplitudes from spinally treated rats (expressed as the percent change from baseline). ∫Phr burst amplitudes from rats pretreated (20 min before) with a MEK inhibitor (U0126, n = 9) were decreased compared with vehicle treatment (n = 7) at 60 min post-AIH. In rats pretreated with PI3K inhibitor (PI-828, n = 6), ∫Phr burst amplitudes increased over baseline at 60 min post-AIH and were not different than vehicle treatment. Hence, MEK activity, not PI3K, is required for pLTF. Values are means ± SE. #Significantly different from vehicle control; †significantly different from MEK inhibitor (P < 0.05).