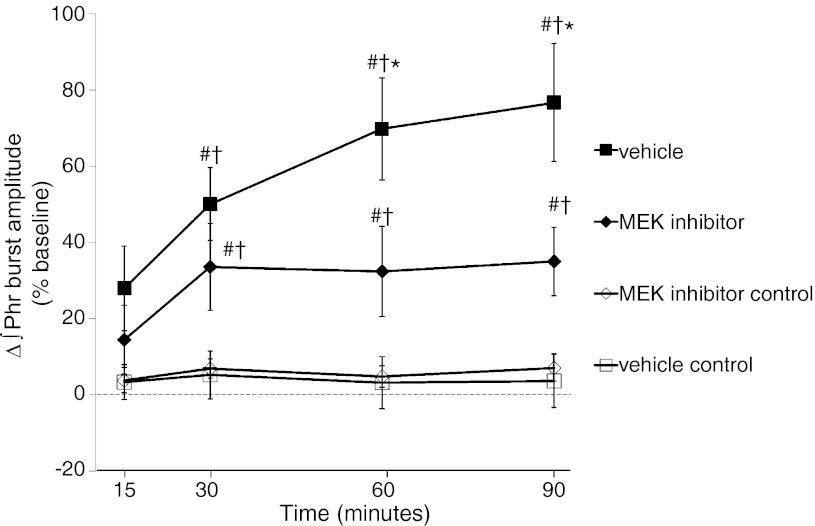
Fig. 6.
Spinal MEK inhibition post-AIH attenuates pLTF expression. Comparisons were made for ∫Phr burst amplitudes from spinally treated rats (expressed as the percent change from baseline). ∫Phr burst amplitudes from rats treated with vehicle (n = 8) immediately after AIH (<5 min) exhibited significant pLTF up to 90 min post-AIH. To test the hypothesis that pLTF maintanence requires MEK activity, rats were given a spinal injection of a selective inhibitor (U0126, 100 μM, n = 8) immediately after AIH. U0126 attenuated ∫Phr burst amplitudes at 60 min post-AIH and beyond, suggesting that continued MEK/ERK activity is required to maintain full pLTF expression. Control rats that received either vehicle (n = 8) or U0126 (n = 8) without AIH exhibited facilitation. Values are means ± SE. *Significantly different from MEK inhibitor; #significantly different from vehicle control; †significantly different from MEK inhibitor control (P < 0.05).