Table 1.
Sequence and biological activities of the native and chemically modified Noxa BH3 peptides.
| Name | Sequencea | Charge | FP assayb Ki (nM) | Cell viabilityc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noxa | AAQLRRIGDKVNLRQKLLN | +4 | 648±128 | 97.6±0.9 |
| 1 | AAC′LRRIGDC′VNLRQKLLNd | +3 | 10±1 | 98.6±4.0 |
| 2 | AAc′LRRIGDC′VNLRQKLLNe | +3 | 54±14 | 100.3±0.2 |
| 3 | AAc′LRAIGDC′VNLRQKLLN | +2 | 23±8 | 85.9±2.2 |
| 4 | AAc′LRAIGDC′VNLAQKLLN | +1 | 28±11 | 72.9±3.2 |
| 5 | AAc′LRAIGDC′VNLAQALLN | 0 | 29±4 | 44.3±0.2 |
| 6 | AmAc′LRRIGDC′VNLRQKLLNf | +3 | 32±3 | 87.3±2.8 |
| 7 | AmAmc′LRRIGDC′VNLRQKLLN | +3 | 22±4 | 80.5±4.7 |
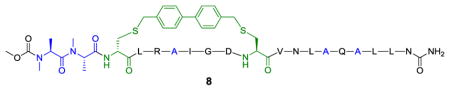
| 8 | AmAmc′LRAIGDC′VNLAQALLNg | 0 | 22±8 | 34.8±0.5 |
Peptides with N-terminal Ala were acetylated while those with N-terminal N-methyl-Ala (Am) were capped with methoxycarbonyl (Moc); all peptides were amidated at the C-termini.
Competitive fluorescence polarization (FP) assay was performed three times to derive average IC50 values along with standard deviations.
Cell viability was measured with ATP assay by treating Mcl-1-overexpressing U937 cells (cultured in RPMI1640 supplemented with 5% FBS) with 20 μM peptides for 48 hours.
C′ denotes Bph-linked L-cysteine.
c′ denotes Bph-linked D-cysteine.
Am = N-methyl-alanine
The structure of 8 is shown as follows: