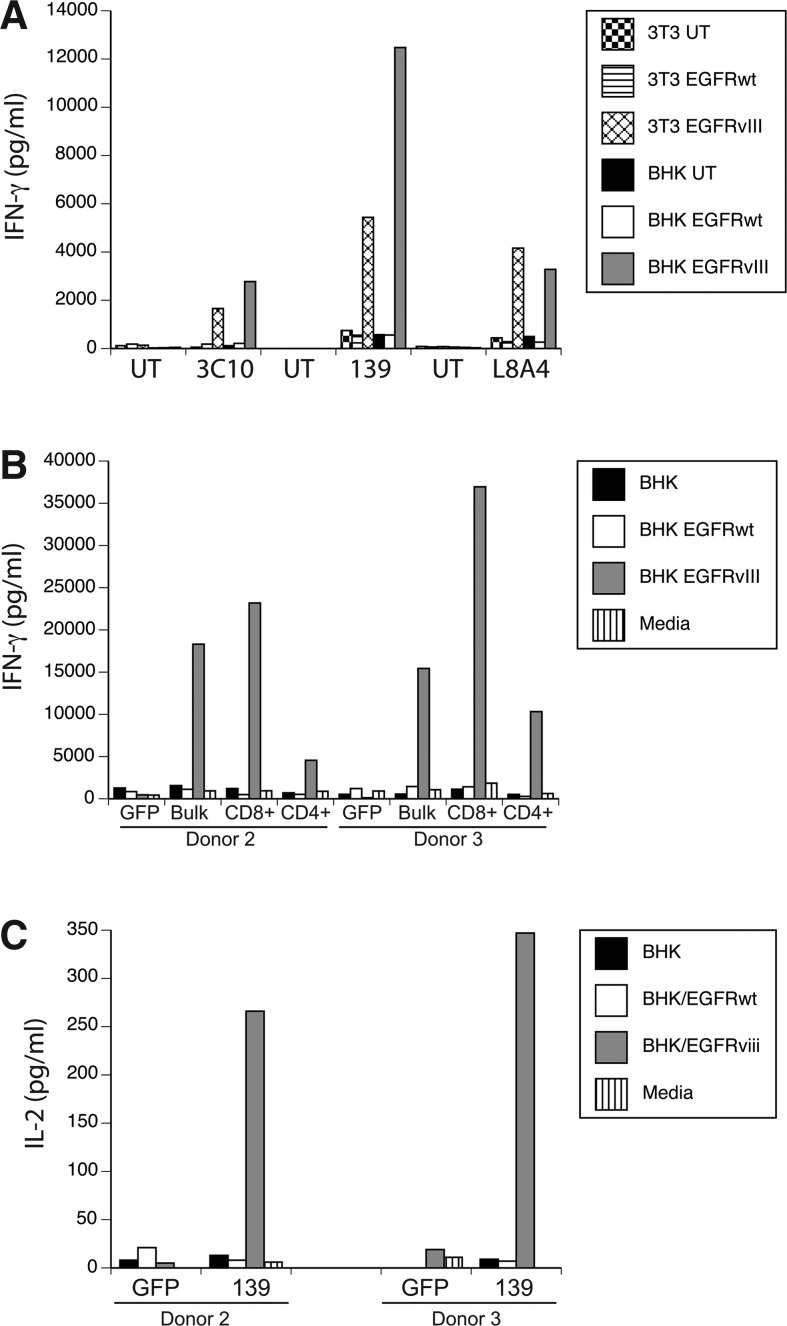
FIG. 2.
Anti-EGFRvIII CAR vector-engineered T cells specifically recognize EGFRvIII-expressing cells. (A) γ-Retroviral vectors expressing the anti-EGFRvIII CARs (from murine mAbs 3C10 and L8A4 and human mAb 139) were used to transduced human T cells, which were cocultured with the indicated target cell lines. Target cell lines NIH-3T3 (3T3) and BHK were engineered with the wild-type EGFR (EGFRwt) or EGFR variant vIII (EGFRvIII) genes, or untransduced (UT). Shown is the resultant IFN-γ production as measured by ELISA (pg/mL, mean of triplicate determinations). (B) T cells from two donors (donors 2 and 3) were transduced with the 139-28Z vector (Bulk) and then bead sorted into CD8- and CD4-enriched (>96% positive) T-cell populations (CD8+ and CD4+). These cells were cocultured overnight with BHK target cells, EGFR wild-type (EGFRwt), or EGFRvIII engineered BHK cells (EGFRvIII) and the amount of IFN-γ produced determined (IFN-γ shown in pg/mL, mean of triplicate determinations). GFP, control vector transduced T cells. (C) CD4+ T cells from panel B were cocultured overnight with BHK target cells, EGFR wild-type (EGFRwt), or EGFRvIII engineered BHK cells (EGFRvIII) and the amount of IL-2 produced determined (IL-2 shown in pg/mL, mean of triplicate determinations). Data are representative of three independent experiments. Differences between recognition of EGFRvIII transduced versus control lines were statistically significant (p<0.01, Student's t test).