Fig. 4.
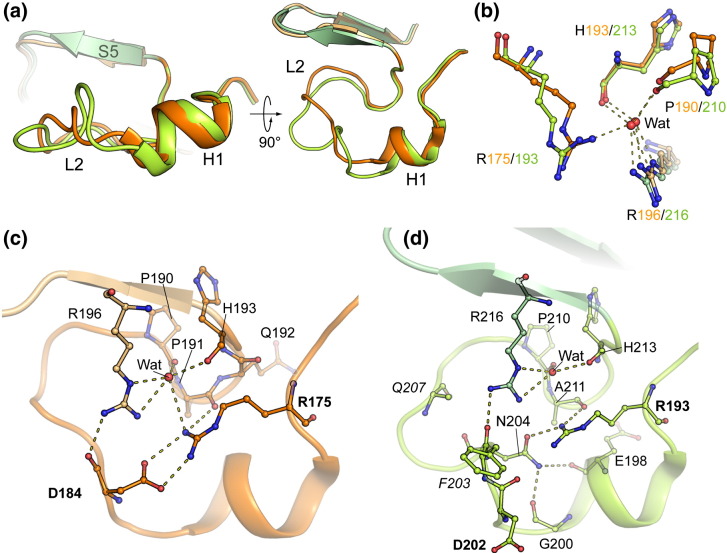
The p73 structure contains a divergent L2 loop. (a) Superposition of the free p53 (orange) and p73 (green) structures highlighting the different L2 loop conformations. (b) In both structures, conserved residues in the L2 loop form hydrogen bonds to a buried, ordered water molecule. (c) Salt bridge and hydrogen bond interactions in the p53 L2 loop. The R175 and D184 positions are highlighted. (d) The p73 L2 loop harbors a two-residue insertion (sequence alignments indicate insertion of p73 F203 and Q207 shown labeled in italics). As a result, the L2 loop structure and hydrogen bonding are changed. Most notably, the p53 R175–D184 salt bridge (equivalent to p73 residues R193 and D202 labeled in boldface) is replaced by p73 R193 interaction with N204. The N204 side chain also forms two hydrogen bonds to the H1 helix that are absent in p53.