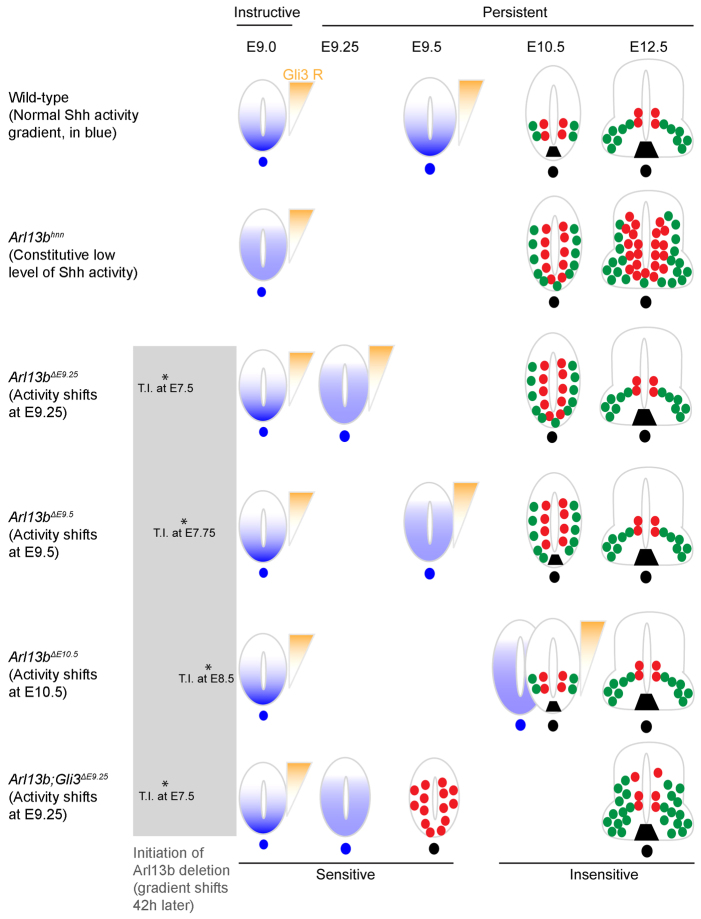
Fig. 7.
Summary of phenotypic analyses. In wild-type neural tube, Shh activity (blue) establishes a ventral-to-dorsal gradient, while a Gli3 repressor activity gradient (orange) is established dorsally at E9.0, and normal patterning is observed at E10.5 and E12.5. In Arl13bhnn, there is a constitutive low level of Shh activity, but normal Gli3 repressor activity, resulting in an expansion of pMN cells and motoneurons that persist to E12.5. In Arl13bΔE9.25 and Arl13bΔE9.5, a normal Shh activity gradient is established initially, but disrupted at E9.25 and E9.5, respectively; however, Gli3 repressor activity is intact. An expansion of pMN cells and motoneurons is detected in E10.5 Arl13bΔE9.25 and Arl13bΔE9.5, but both pMN cells and motoneurons are expressed normally at E12.5. In Arl13bΔE10.5, Shh activity gradient is disrupted at E10.5, but patterning is normal, suggesting that cells are no longer sensitive to changes in Shh activity after E10.5. In Arl13b Gli3ΔE9.25, Gli3 repressor is absent and there is a constitutive low level of Shh activity at E9.0, resulting in an expansion of Olig2 at E9.5 and a slight dorsal expansion of Olig2 and HB9 cells at E12.5. Lines on the top indicate Shh plays an instructive role at E9.0, and switches to become a persistent signal after E9.25. Asterisks represent the time points when tamoxifen is injected into pregnant females. Blue and orange shading demonstrate Shh and Gli3 repressor activity, respectively. In E9.5, E10.5 and E12.5 neural tube, red and green circles represent cell fates that are resulting from Shh activity: red circles are pMN cells; green circles are motoneurons. Black trapezoid is the floor plate. T.I., tamoxifen injection.