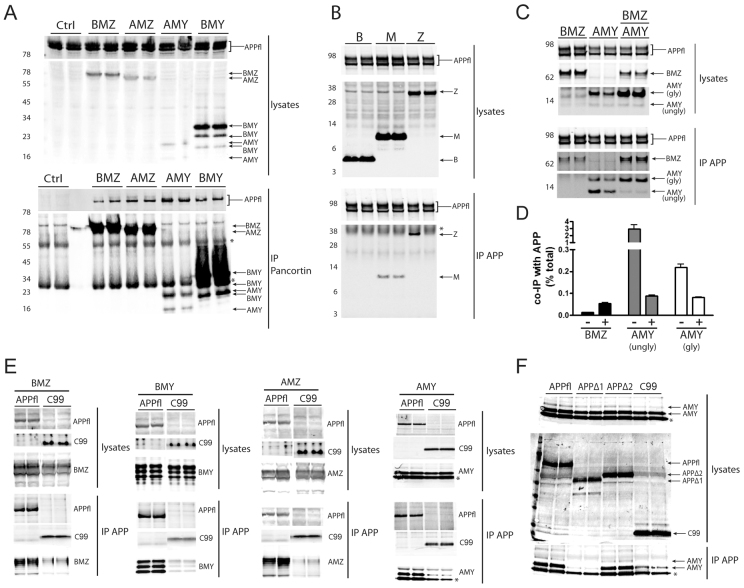
Fig. 2.
APP and pancortins biochemically interact. Western blots for APP (anti-APP, C9) and FLAG-tagged pancortin (anti-FLAG, M2) are shown for both the input (lysates) and the immunoprecipitated products. Immunoprecipitations of lysates for FLAG (M2) are shown in A and for APP (C9) in B-F. Asterisks represent non-specific or cross-reactive IgG bands. (A) Western blots of lysates of HEK293-APP695 cells transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged pancortin isoforms or vector alone (ctrl). (B) Western blots of lysates and IPs of HEK293-APP695 cells transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged pancortin domains B, M and Z. (C) Western blots of lysates and IPs of HEK293-APP695 cells transiently transfected with BMZ and AMY isoforms alone or together. (D) Quantification of the percent of BMZ and AMY co-immunoprecipitated with APP relative to the total amount of each isoform in the lysate for BMZ and both the unglycosylated (lower band, ‘ungly’) and glycosylated (upper band, ‘gly’) forms of AMY when BMZ and AMY were expressed separately (−) or together (+). (E) Western blots of lysates and IPs of HEK293 cells transiently transfected with each of the pancortins and either full-length APP (APPfl) or a C-terminal fragment of APP (C99). (F) Western blots of lysates and IPs of HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the AMY isoform of pancortin and either full-length APP, APPΔ1 (lacking residues 36-289), APPΔ2 (lacking residues 288-493) or C99.