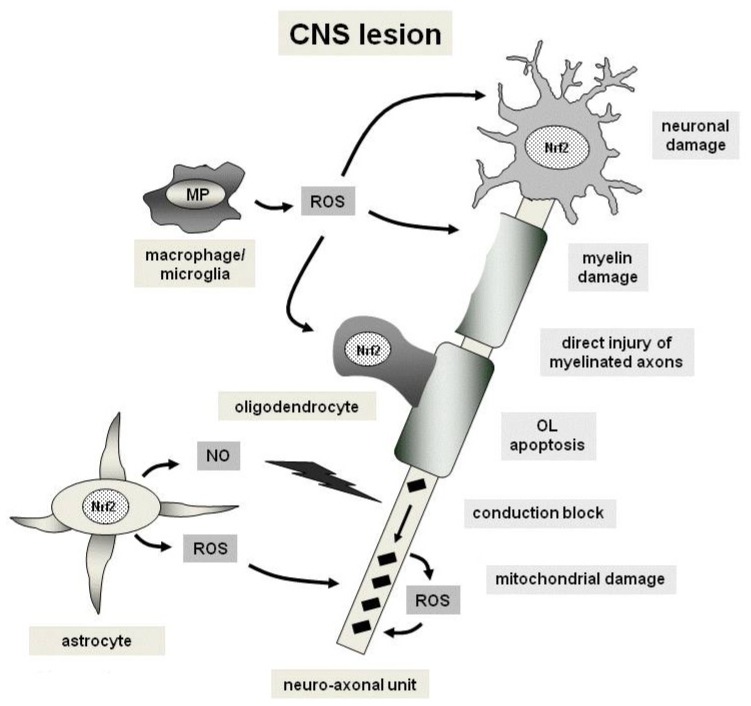
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of oxidative injury and cytoprotection in a demyelinating Central Nervous System (CNS) lesion. Free radicals comprise nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen as well as nitrogen species (Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) or Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS), respectively) which are mainly produced by macrophages, microglia and astrocytes. ROS and RNS lead to damage of neurons, axons, myelin and oliogdendrocytes (indicated by arrows). This process also may involve mitochondrial damage. Black squares indicate mitochondria which accumulate in injured axons. The cytoptrotective transcription factor Nrf2 is present in neurons, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes as part of the cellular anti-oxidative response. Abbreviations: OL, oligodendrocyte; MP, myeloperoxidase.