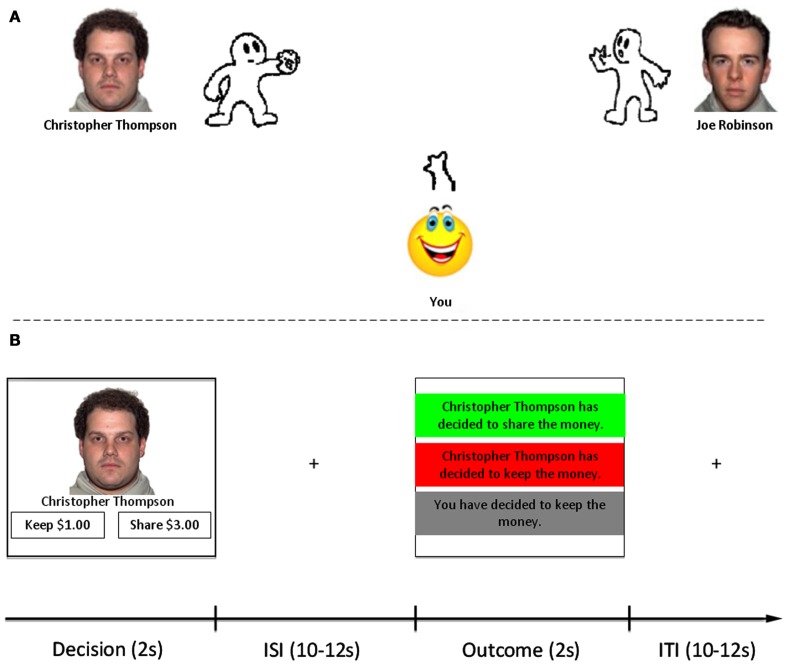
Figure 1.
Task structure. (A) Participants were first introduced to three different partners with whom they would later interact with in the trust game. Participants played three separate versions of Cyberball. The character on the right side of the screen was consistent across all three versions (control). The face and name of the character on the left side changed in each version, as did character ball-tossing behavior to be depicted as good, bad, neutral. (B) After Cyberball, participants played an iterated trust game adapted from Delgado et al. (2005a). Trials with each partner were interleaved within functional scanning runs, as were lottery trials (non-social control). Each trial consisted of a Decision Phase (2 s) in which they were to choose whether to keep or share money with their partner (or not play/play the lottery). After a variable ISI (10–12 s), the Outcome Phase (2 s) was presented consisting of feedback in the form of partner reciprocation/defection, or null feedback indicating defection by the participant. All trials were separated by a 10–12 s ITI.