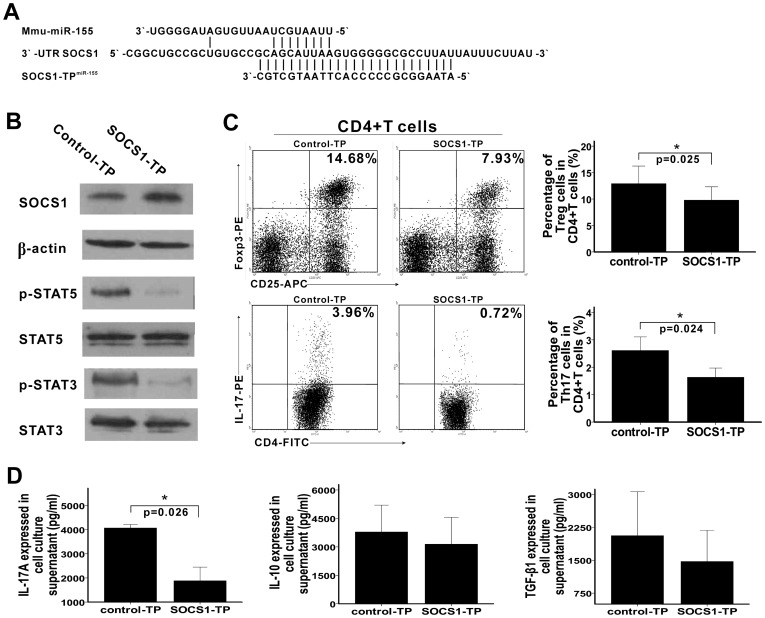
Figure 4. SOCS1-TPmiR-155 inhibits the function of miR-155 during Treg and Th17 cells differentiation.
A. Sequences of mmu-miR-155, 3′-UTR SOCS1, and SOCS1-TPmiR-155 are shown in the schematic. As shown, seed sequences of mmu-miR-155 complementary to 3′-UTR SOCS1, whereas sequences of SOCS1-TPmiR-155 completely complementary to 3′-UTR SOCS1 and over-lapped the binding site of miR-155 in the 3′ UTR of SOCS1. B. The percentages of Treg and Th17 were determined by flow cytometry 4 days after SOCS1-TPmiR-155 and control-TPmiR-155 (shown in the figures as SOCS1-TP and control-TP, respectively) were transfected. Treg and Th17 cells were gated with CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ and CD4+IL-17+, respectively. Typical FACS pictures from a single case are shown in the left. The collective results of three independent experiments are shown in the right as mean ± SD. C. 4 days after SOCS1-TPmiR-155 and control-TPmiR-155 were transfected, the levels of IL-17A, IL-10, and TGF-β1 in cell culture supernatant were quantified by ELISAs and the collective results are shown as mean ± SD. D. 4 days after SOCS1-TPmiR-155 and control-TPmiR-155 were transfected, the levels of the transcripts involved in Treg and Th17 cells differentiation were also detected by western blotting. Data represent three independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.