Figure 2. ORAI1, STIM1 and STIM2 control SOCE and cytokine production in CD4+ T cells.
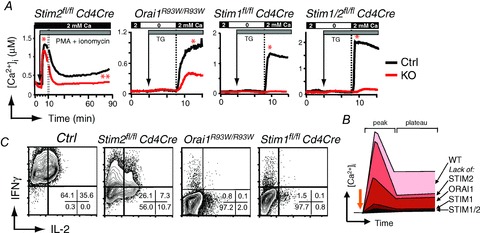
A, T cell-specific deletion of STIM2 in CD4+ T cells from Stim2fl/fl Cd4Cre mice does not interfere with the peak of Ca2+ influx (*) but impairs sustained SOCE (**) compared to wild-type control (Ctrl) T cells. Gradually more severe defects in SOCE are observed (in this order) in ORAI1-, STIM1- and STIM1/2-deficient CD4+ T cells (from Oh-Hora et al. 2008; McCarl et al. 2010 and authors unpublished observations). T cells were stimulated with PMA (10 nm), ionomycin (0.5 μm) and thapsigargin (TG, 1 μm) in Ringer solution containing 0 or 2 mm Ca2+ as indicated. In Orai1R93W knock-in mice, the endogenous Orai1 gene was replaced with a mutant (Arg → Trp) allele that encodes a non-functional ORAI1 protein. B, summary of SOCE levels in ORAI/STIM-deficient murine CD4+ T cells. C, cytokine production by CD4+ T cells from the indicated mice that were stimulated for 6 h with PMA and ionomycin and analysed by intracellular cytokine staining in flow cytometry (from Oh-Hora et al. 2008; McCarl et al. 2010; Copyright 2010. The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.). Note that >99% of wild-type Ctrl T cells express IFNγ or IFNγ and IL-2, whereas this percentage is gradually reduced in STIM2-, ORAI1- and STIM1-deficient CD4+ T cells.
