Figure 4. Inhibition of Ca2+-dependent inactivation of ICa by calmodulin domain peptide290−309 and Bay K is associated with enhanced suppression of ICa by anoxia.
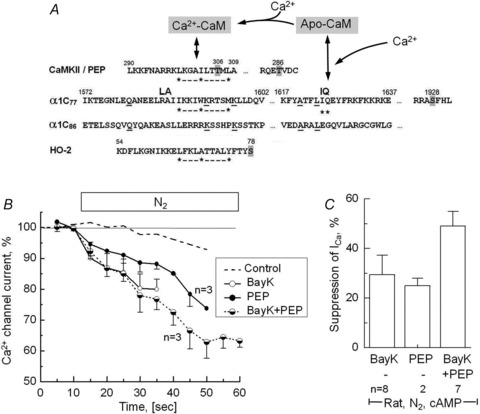
A, putative CaM-binding (IQ and hydrophobic 1–5–10 motifs) and phosphorylation sites (grey highlight) in the partial AA sequences of CaMKII, peptide290−309 (PEP), wild-type and mutant α1c subunits of the Ca2+ channel (α1c77 and α1c86) and haem oxygenase (HO-2) (Colbran, 1993; Rhoads & Friedberg, 1997; Soldatov et al. 1997; Boehning et al. 2004). B, time course of suppression of ICa upon removal of extracellular O2 in cAMP-dialysed rat cardiomyocytes that in addition were dialysed with 100 μm PEP, treated with 1 μm Bay K8644 (BayK) or both. For comparison purposes, ICa in cardiac control cells dialysed with 0.2 mm of cAMP is reproduced from Fig. 3A (dashed line). C, comparison of the anoxic suppressions of ICa in cardiomyocytes measured after 60–90 s of hypoxia (during recording of I–V relations). A, amino acid sequences of α1c77 and α1c86 subunits.
