Figure 6. Model 2 for ClC-2 gating.
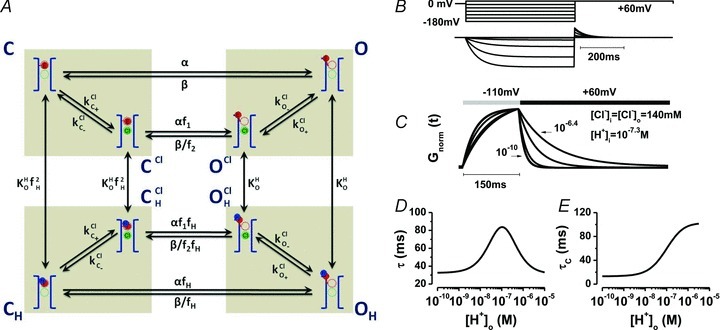
A, kinetic model built according to Scheme II that couples movement of the fast gate to Cl− occupancy of the pore. Rectangular boxes indicate four conformations: C = closed unprotonated, O = open unprotonated, CH = closed protonated and OH = open protonated. Scen and Sext anion binding sites are represented by dashed green and red circles, respectively. Cl− is represented by a green sphere, H+ by a blue sphere and the fast gate by a red sphere. Protonation of the fast gate by 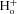 is indicated by a blue sphere attach to a red sphere. Transitions between Cl−-free and Cl−-bound states are dictated by Vm-dependent rate constants. Transitions between unprotonated and protonated states are characterized by Vm-independent equilibrium constants
is indicated by a blue sphere attach to a red sphere. Transitions between Cl−-free and Cl−-bound states are dictated by Vm-dependent rate constants. Transitions between unprotonated and protonated states are characterized by Vm-independent equilibrium constants 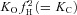 and KO, respectively. Fast gate is open by electrostatic repulsion when either a Cl− (f1 = 151) or H+ ion is bound (fH = 8.46). B, simulated ionic currents from +60 mV to −180 mV, in 40 mV increments according to the voltage protocol shown on top. ICl(t) were simulated for [Cl−]i = [Cl−]o = 140 mm, pHo = pHi = 7.3. C, simulated time course of Gnorm at −110 and +60 with [H+]o from = 10−10
m to = 10−6.4
m. D, opening time constant vs.[H+]o. E, closing time constant vs.[H+]o. Simulations were done using the parameter set listed in Table 1.
and KO, respectively. Fast gate is open by electrostatic repulsion when either a Cl− (f1 = 151) or H+ ion is bound (fH = 8.46). B, simulated ionic currents from +60 mV to −180 mV, in 40 mV increments according to the voltage protocol shown on top. ICl(t) were simulated for [Cl−]i = [Cl−]o = 140 mm, pHo = pHi = 7.3. C, simulated time course of Gnorm at −110 and +60 with [H+]o from = 10−10
m to = 10−6.4
m. D, opening time constant vs.[H+]o. E, closing time constant vs.[H+]o. Simulations were done using the parameter set listed in Table 1.
