Figure 1. Isolated coronary arterioles were dilated in response to ACh in a concentration-dependent manner.
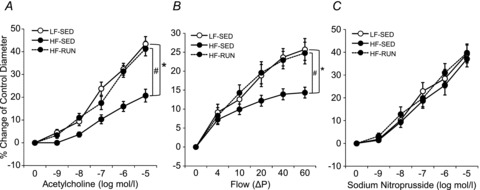
A, ACh-induced vasodilatation was significantly attenuated in HF-SED (n = 11) mice compared with LF-SED mice (n = 7). However, voluntary wheel running prohibited the development of impaired ACh-induced vasodilatation in coronary arterioles during high-fat feeding in HF-RUN (n = 8). B, flow-induced vasodilatation was lower in HF-SED mice compared with LF-SED mice, but it was opposed by voluntary wheel running in high-fat fed mice (HF-RUN). C, the endothelium-independent vasodilator, SNP (NO donor)-induced vasodilatation was not significantly different among the 3 mice groups. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. LF-SED, #P < 0.05 vs. HF-SED.
