Figure 1.
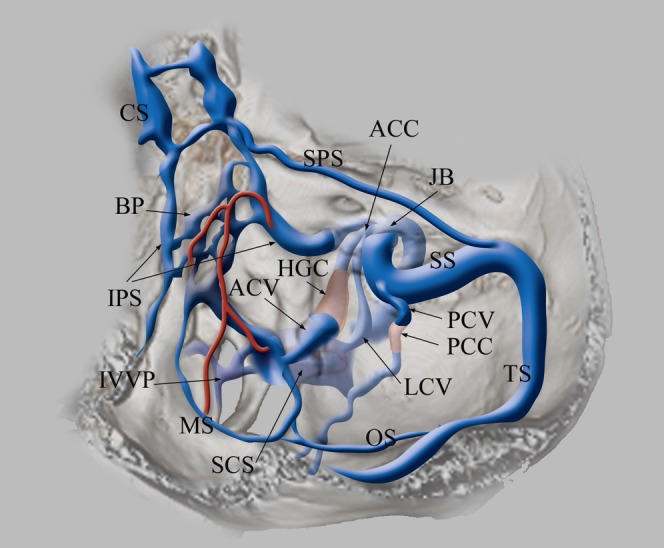
Schematic drawing of the veins at the craniocervical junction. The inferior petrosal sinus (IPS) originates from the posterosuperior aspect of the cavernous sinus (CS), runs along the petroclival fissure and drains into the jugular bulb (JB). Basilar plexus (BP) lies on the clivus with connecting bilateral IPS. The anterior condylar vein (ACV) and lateral condylar vein (LCV) originate from the medial aspect of the JB, forming an anterior condylar confluence (ACC). ACV runs medially through the hypoglossal canal (HGC) and drains into the lateral part of the marginal sinus (MS). MS is contiguous to the medial part of the suboccipital cavernous sinus (SCS). LCV runs posterolaterally and flows into SCS. The posterior condylar vein (PCV) originates from the sigmoid sinus (SS), runs through the posterior condylar canal (PCC) and flows into SCS. SCS lies under the occipital bone surrounding the horizontal portion of the vertebral artery. The occipital sinus (OS) originates from the torcular herophili, confluence of transverse sinus (TS) and straight sinus and drains into the posterior part of MS. MS is the round-shaped sinus surrounding the foramen magnum. MS and the medial part of SCS are connected to the internal vertebral venous plexus (IVVP).
