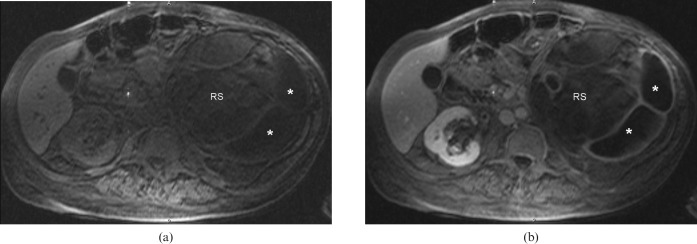
Figure 3.
Axial chemically selective fat-saturation gradient-echo T1 weighted images before (a) and after (b) the intravenous administration of gadolinium chelate demonstrate complete loss of signal of the structure expanding the left renal sinus (RS) that was hyperintense on the in- and out-of-phase T1 weighted images, confirming the fatty nature of this tissue. The dilated renal calyces peripherally (*) fail to demonstrate excretion on the post-contrast images.