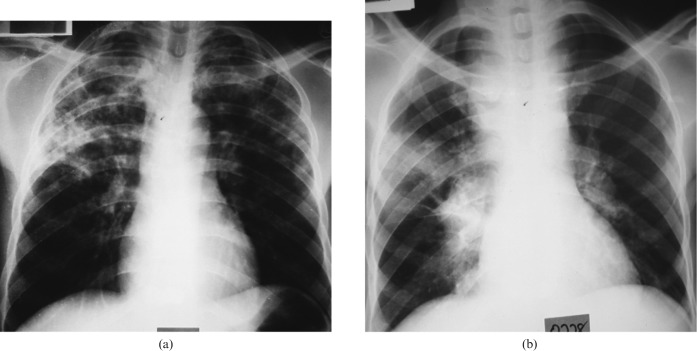
Figure 4.
(a) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-seropositive patient with a CD4+ T-cell count of 173 cells mm–3 and tuberculosis (TB). A posteroanterior chest radiograph shows patchy opacities in the upper and mid zones bilaterally. (b) HIV-seropositive patient with TB and a CD4+ T-cell count of 1 cell mm–3. A posteroanterior chest radiograph shows enlarged right paratracheal, tracheobronchial and bilateral hilar lymph nodes and a homogeneous opacity in the right mid zone, giving a pattern similar to a primary TB.