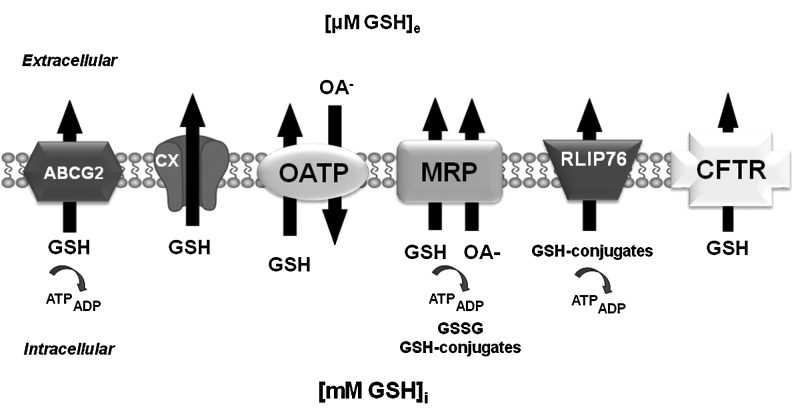
FIG. 4.
Plasma membrane GSH efflux pumps. Distinct candidates have been proposed to act as GSH transporters. The MRPs act as ATP-dependent cotransporters of GSH (coupled to the extrusion of an OA−), GSSG, and GSH conjugates. MRP1 can transport GSH alone, but this requires its stimulation by xenobiotics. The OATPs were initially proposed to act as the GSH/OA− exchanger, where GSH efflux is thought to be driven by its electrochemical gradient across the plasma membrane, and stimulated by the presence of extracellular OA−. Other proposed candidates for GSH efflux are the members of the ABC family of transporter CFTR and BCRP/ABCG2, hemichannel connexins (CX), and RLIP76. Energy dependency of GSH transport by BCRP/ABCG2 has not yet been confirmed. ABC, ATP-binding cassette; MRP, multidrug resistance protein; OA−, organic anion; OATP, organic anion transporting polypeptide; RLIP76 (RALBP1), Ral-binding, Rho/Rac-GAP and Ral effector.