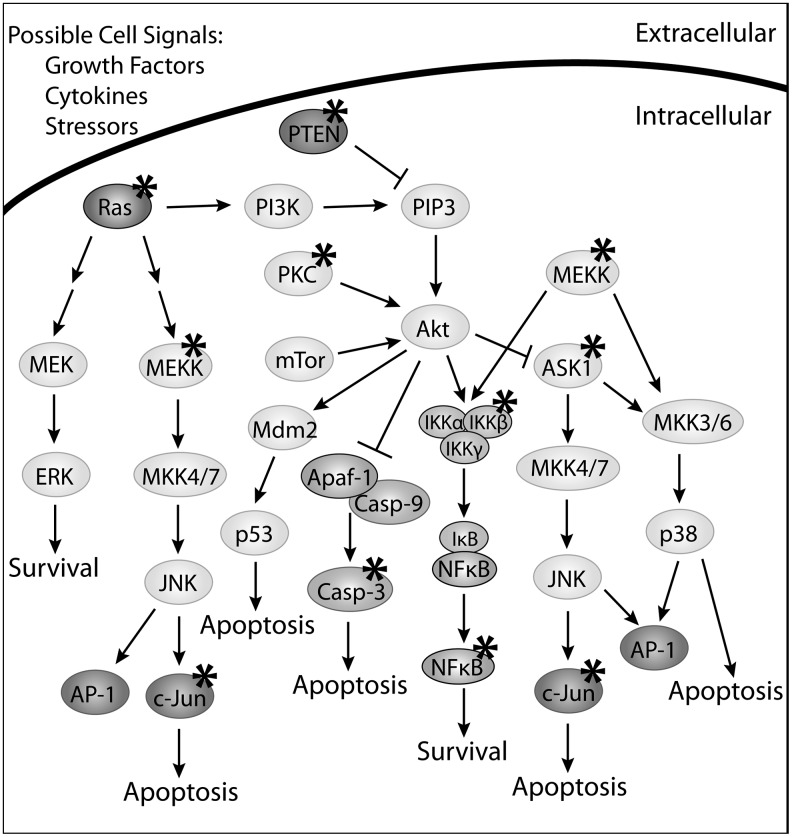
FIG. 4.
Signaling pathways mediated by rat sarcoma (Ras) and protein kinase B (Akt). Ras and Akt are key apoptosis mediators responsible for several regulatory pathways. There is experimental evidence to implicate that many of the proteins in these pathways as being regulated by Grx and protein glutathionylation, as indicated by an asterisk (*). Depending on the cellular insult, cell type, and protein target, alterations in protein glutathionylation may result in cell survival or apoptosis. Ras is responsible for mediating the Akt, mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase kinase (MEKK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and MKK/JNK pathways. Glutathionylated Ras is an active form of this protein that can lead to increased Akt activity and therefore cell survival via the nuclear factor kappa-light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB) cascade. When Grx deglutathionylates Ras, this can result in activation of the MEKK pathway and inhibition of Akt, resulting in apoptosis. An upstream regulator of Akt is phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), which is responsible for dephosphorylating PIP3, preventing the activation of Akt. PTEN-SSG is the inactive form of this protein, and is no longer able to dephosphorylate PIP3. Therefore, in the absence of Grx, PIP3 is phosphorylated and capable of activating Akt, resulting in cell survival. Like PTEN-SSG, protein kinase C (PKC) is also inhibited when it is glutathionylated. However, this protein modification prevents PKC's ability to phosphorylate and activate Akt, causing apoptosis. The downstream effectors of Akt include apoptosis signaling kinase (ASK1), Apaf-1/caspase-9, and the NFκB pathway. Many of these proteins can also be regulated by Grx and protein glutathionylation. Grx is capable of binding to ASK1 resulting in the inhibition of this protein and ultimately cell survival. Grx regulates the NFκB pathway via deglutathionylation of IKK and NFκB. Grx is implicated in many of the cellular survival/death signaling mechanisms, evident by the number of proteins potentially regulated by Grx and glutathionylation in these pathways.