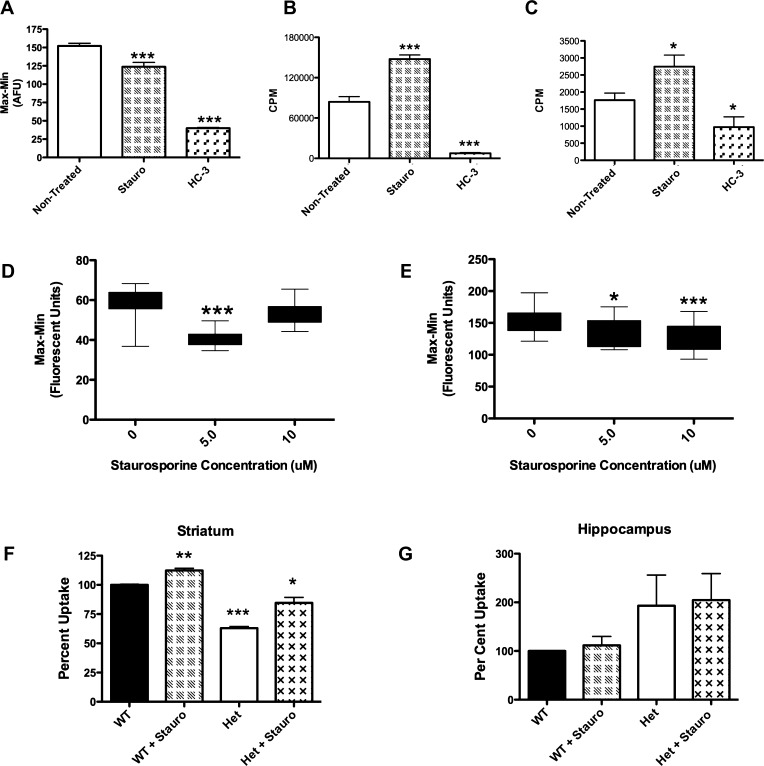
Figure 7.
Establishment of secondary assays to verify compounds discovered using the choline-induced membrane potential assay: Staurosporine as a model CHT activator. (A–E) Secondary assays performed on the CHT LV-AA cell line. (A) The fluorescent peak response of the choline-induced membrane potential assay (bar 1) is inhibited by HC-3 (bar 3). Treatment of CHT LV-AA cells with 5 μM staurosporine for 60 s before choline application significantly reduced the fluorescent signal response mediated by Na+ flow through the transporter (p < 0.0001). (B) Following a successful HTS campaign, CHT active compounds will be initially screened for specificity through a traditional 3H-choline uptake assay adapted to a 96-well format (TopCount Perkin-Elmer). As shown in Figure 4 and Table 2, staurosporine was found to increase choline uptake through a KM mechanism (210 nM choline, p < 0.0001). C) As an alternative, a real-time measurement of [3H]-choline uptake in live cells via Scintillation Proximity Assay (SPA) may also be utilized, but this assay has a lower measured uptake signal. SPA results replicate the uptake finding (p < 0.05). (D–E) The concentration of applied choline impact response to compounds in the choline-induced membrane potential assay: (D) 5 μM, but not 10 μM, staurosporine treatment significantly decreased the membrane potential change induced with 410 nM choline (p < 0.0001). (E) Application of 10 μM choline produced a fluorescence response that was reduced in the presence of both 5 μM and 10 μM staurosporine. A greater reduction in fluorescent response is found treating with 10 μM staurosporine, although the 5 μM treatment is still significant (p < 0.01 and p < 0.0001). (F) Following verification in secondary assays, compounds found in this HTS campaign will be screened against prepared mouse synaptosomes. Staurosporine significantly increased the uptake of [3H]-choline in mouse striatal synaptosomes (p = 0.003, n = 3, Student’s t-test). The CHT heterozygous animal (±) could also be stimulated by staurosporine (p = 0.01) and demonstrated a reduced basal [3H]-choline uptake capacity (p < 0.001). (G) In contrast, [3H]-choline uptake measurements from hippocampal synaptosomes were staurosporine-insensitive. Although the CHT ± animal had an elevated uptake, this was not significant. Significant change was determined by Student’s t-test analyses of all trials n = 3–5 for all assays and reported under values as *–*** for p values less than 0.05–0.001.