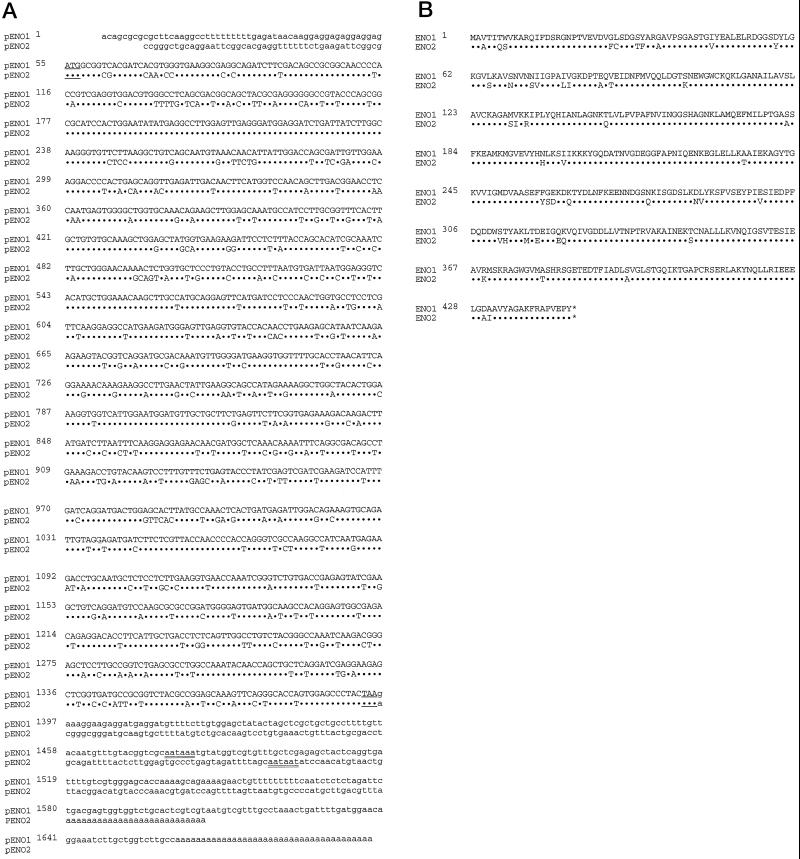
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment of maize enolase pENO1 and pENO2. A, The complete nucleotide sequence of ENO2 is aligned with that of ENO1. The nontranslated regions are in lowercase and the coding region is in uppercase. The initiation and termination codons are underlined. The putative consensus AATAAA sequence, which in animals serves as a signal for poly(A+) tail addition, also exists in the 3′-untranslated region of ENO1 and in a slightly modified form (AATAAT) in ENO2, and is double-underlined. B, The deduced polypeptide sequence of pENO1 is compared with that of pENO2. The asterisks indicate the termination codons. In both A and B, identical sequences in the coding regions are indicated by dots. {/ANNT;84480n;69696n;92928n;118272n}