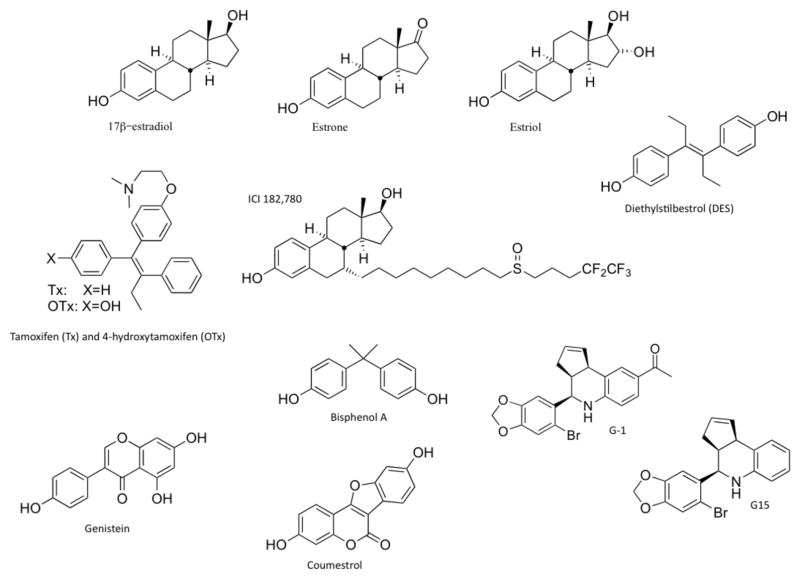
Figure 1.
Structures of selective and nonselective estrogen receptor ligands. Compounds shown include the three major physiological forms of estrogen (17β-estradiol, estrone and estriol); the anticancer agent tamoxifen and its active metabolite 4-hydroxytamoxifen (which is both a selective estrogen receptor modulator and an agonist for GPER); fulvestrant, a selective estrogen receptor downregulator and agonist for GPER; diethylstilbestrol, a nonselective GPER agonist; the phytoestrogens genistein and coumestrol; and the xenoestrogen bisphenol A. Also shown are G-1 (a selective GPER agonist) and G15 (a selective GPER antagonist). Abbreviation: GPER, G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1.