Figure 6. .
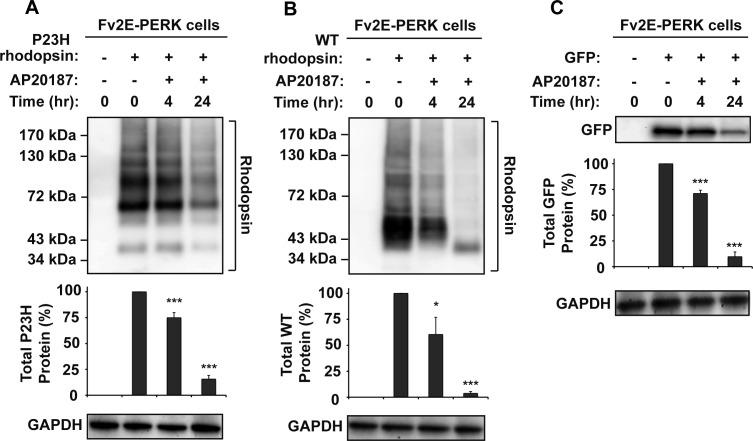
Chemical–genetic activation of PERK reduced WT and P23H rhodopsin protein levels. (A) P23H rhodopsin was transfected into cells expressing drug-sensitized Fv2E-PERK, and AP20187 (2 nM) was applied as indicated. (B) WT rhodopsin was transfected into cells expressing Fv2E-PERK, and AP20187 (2 nM) was applied as indicated. (C) GFP was transfected into HEK293 cells expressing Fv2E-PERK, and AP20187 (2 nM) was applied as indicated. (A–C) Rhodopsin or GFP protein levels were detected by immunoblotting and quantified by a commercial image acquisition and analysis software program (VisionWorks LS Software). GAPDH levels were assessed as a protein loading control. Immunoblots are representative of three independent experiments. Statistical significance (mean ± SD; n = 3) was determined by Student's t-test, and is denoted by asterisks: *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 compared with the cells expressing WT or P23H rhodopsin without the treatment of AP20187.