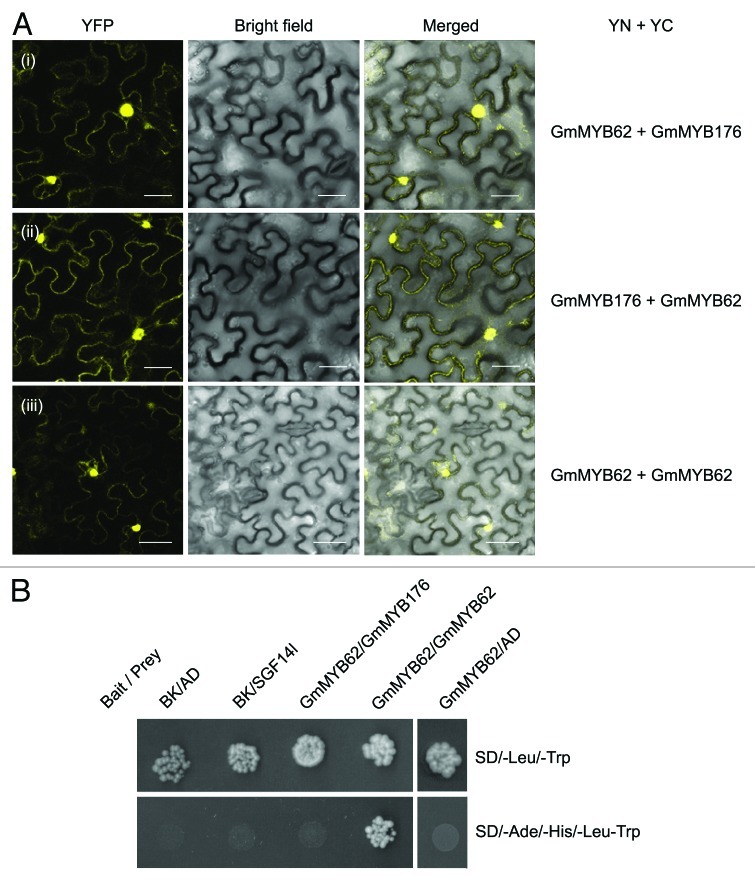
Figure 2. GmMYB62 forms a homodimer and interacts with GmMYB176 in planta. (A) BiFC assay to demonstrate the interaction between GmMYB62 and GmMYB176 and GmMYB62 monomers. N. benthamiana leaves co-transformed with constructs of genes fused to N-terminal (YN) or C-terminal (YC) half of YFP, (as indicated) were imaged 48 h after infiltration, using confocal microscope. (i) GmMYB62-YN+ GmMYB176-YC; (ii) GmMYB176-YN+GmMYB62-YC; (iii). GmMYB62-YN+ GmMYB62-YC. Images are shown as YFP, bright field only and merged YFP and bright-field of epidermal N. benthamiana leaf cells. Scale bars indicate 40 µm. (B) Y2H assay showing interaction between the GmMYB62 monomers. Yeast cells were co-transformed with combination of DNA-binding domain (BK, bait) and activation domain (AD, prey) fused constructs as indicated. SD/-Leu/-Trp and SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp correspond to dropout medium lacking Trp and Leu and Ade, Trp, Leu and His, respectively. A 100 fold diluted co-transformed yeast cultures were spotted on SD/-Leu/-Trp and SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp plate and incubated at 30°C for 5 d. Positive interactions result in yeast growth on the SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp plate.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.