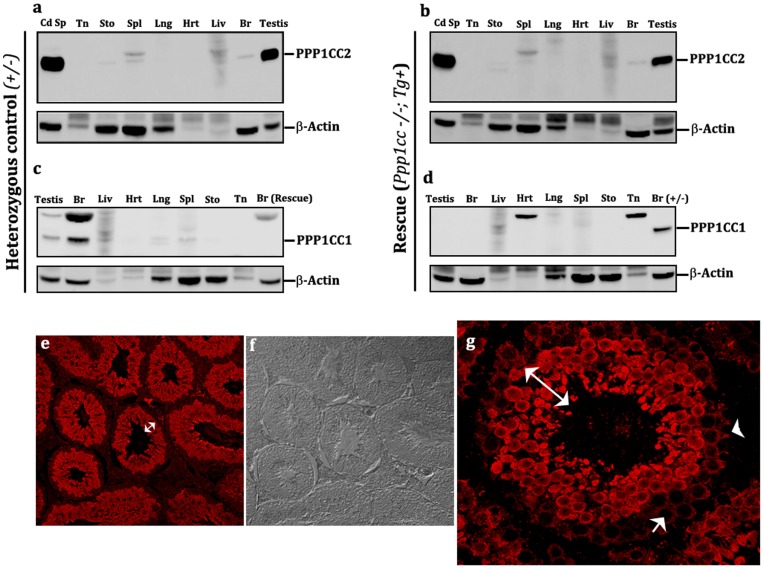
Figure 2. Testis specificity of the 2.6 kb endogenous promoter fragment.
(a, b) Tissue western blot showing the testis specificity of the Ppp1cc gene promoter. PPP1CC2 expression is detected in high amounts in testis and relatively low amounts in brain (Br), spleen (Spl), liver (Liv) in rescue males, comparable to the positive control pattern of expression. No PPP1CC2 reactivity was observed in other somatic tissues studied, including tongue (Tn), stomach (Sto), lungs (Lng) and heart (Hrt). (c, d) Multi-tissue western blot analysis of PPP1CC expression in rescue lines vs. control animals. The absence of PPP1CC1 expression in the testis and brain confirms the Ppp1cc null background of the rescue mice in comparison to control mice where the isoform is expressed. (e, f, g) Immunohistochemistry of testis sections from endogenous promoter- transgenic rescue lines (eTg), showing a wild-type pattern of PPP1CC2 localization in the testis. Double headed (white) arrows indicate PPP1CC2 expression in developing germ cells. Arrow heads points towards its absence in sertoli cells, spermatoginia, pre-leptotene and leptotene spermatocytes. Images were obtained at 20×(e and f) and 60×(g) using confocal fluorescent microscopy. These images are representative observations taken from multiple sections of all three eTg lines (M7, F1 and F10) and several different testis preparations.