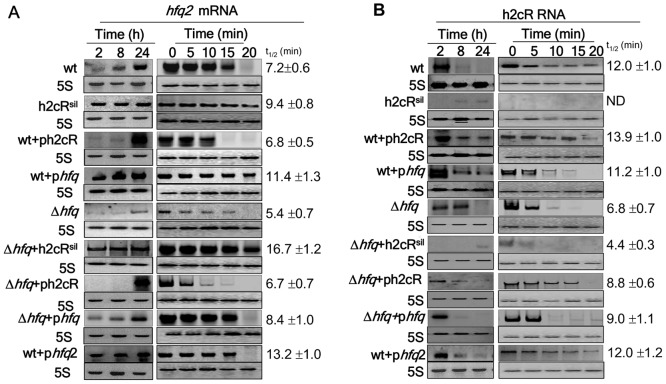
Figure 2. h2cR regulates hfq2 mRNA levels.
Northern blot analysis of the effects of h2cR overexpression (+ph2cR) or silencing (h2cRsil) on (A) hfq2 mRNA levels (left panel) and hfq2 mRNA stability (right panel) or (B) h2cR sRNA levels (left panel) and h2cR sRNA stability (right panel) in the wt, the Δhfq mutant, and derivative strains. h2cR silencing or overexpression was achieved by means of expressing from a pBAD inducible plasmid a 104 nt truncated form of an h2cR-complementary RNA with a CCA trinucleotide extension, or the h2cR sRNA, respectively. The hfq mutant strain (Δhfq) and derivative strains overexpressing hfq (Δhfq +phfq) or hfq2 (Δhfq+phfq2) from a pBAD inducible plasmid [45] were also used to access the possible roles of Hfq, or Hfq2 on hfq2 mRNA and h2cR expression and stability, respectively. RNA decay experiments were conducted using total RNA obtained from cells grown for 2-h (h2cR) or 24-h (hfq2 mRNA). After addition of rifampicin (time 0), samples were taken at the indicated time. Half-life times (t1/2) were calculated by least-square fitting to the linear part of the logarithm of the percentage of remaining RNA versus time. Values indicated are the means of three independent experiments.