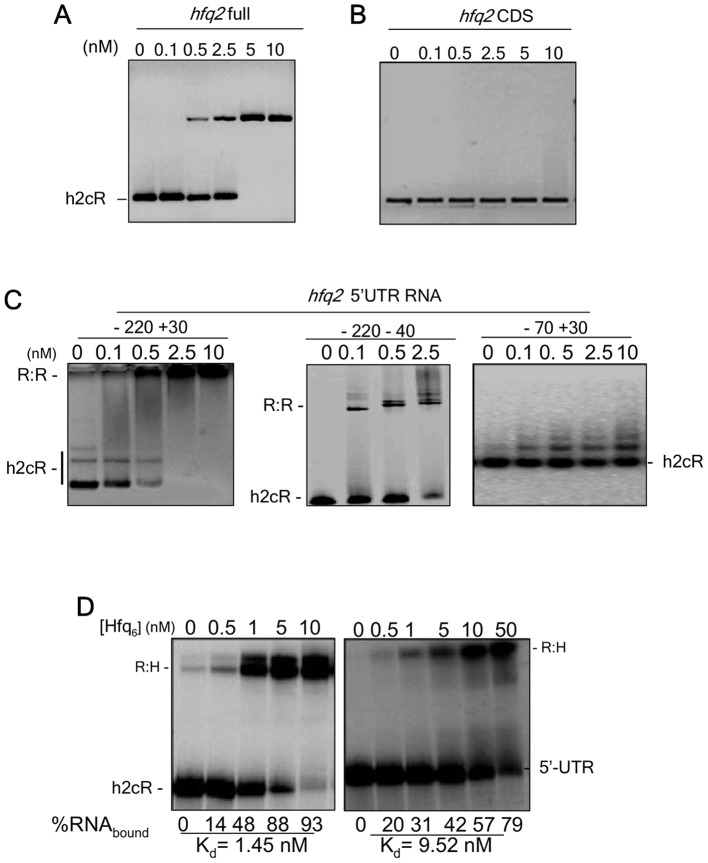
Figure 4. h2cR interacts specifically with the 5′UTR of hfq2 mRNA.
(A) EMSA experiments using 2.5 nM of the h2cR together with the indicated amounts of the hfq2 full transcript or (B) the hfq2 coding sequence; (C) EMSA experiments using with 2.5 nM of h2cR, together with the indicated amounts of the hfq2 5′UTR derivatives full 5′-UTR (nt −220 to +30), the RNA segment spanning nt −220 to −40 of the 5′-UTR, or the RNA segment spanning nt −70 to +30 of the 5′-UTR. For the full 5′-UTR and the RNA segment spanning nt −70 to +30 of the 5′-UTR 0, 0.1, 0.5, 2.5 or 10 nM of the respective 5′-UTR RNA derivatives were used, while for the RNA segment spanning nt −220 to −40 of the 5′-UTR 0, 0.1, 0,5, or 2.5 nM of RNA were used. (D) Ability of Hfq to bind 2.5 nM of h2cR (left panel) or the hfq2 5′-UTR (right panel), as evaluated by EMSA assays using the indicated concentrations of the hexameric form of Hfq. Apparent Kd values were calculated based on a semi-log plot of the RNA binding ratio versus protein concentration, using a exponential fit.