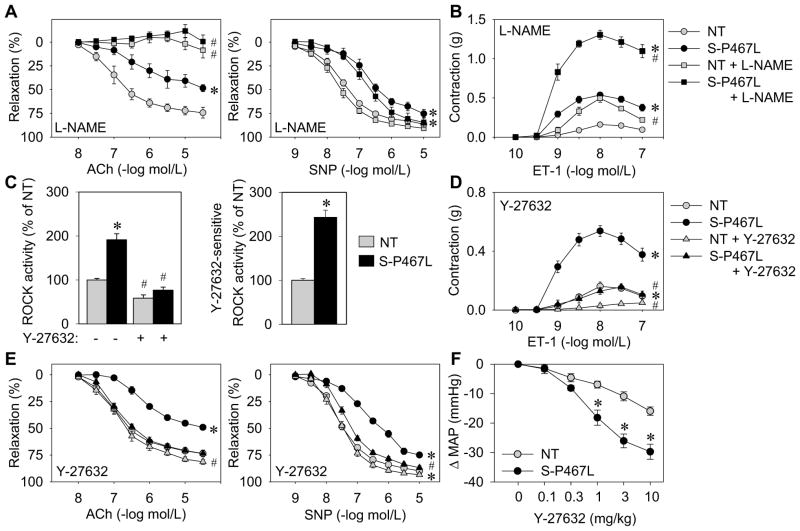
Figure 1. Interference with PPARγ causes increased Rho-kinase activity.
Isometric tension was measured on aortic rings from S-P467L (black) and NT littermates (grey). (A–B) Dose-dependent relaxation (following pre-contraction with prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α)) in response to acetylcholine (Ach) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) (A), contraction in response to endothelin 1 (ET-1) (B) was recorded in the absence or presence of NOS inhibitor (30 min pre-incubation; L-NAME, 100 μmol/L) (n=6–12). (C) ELISA of phospho-Thr696 MYPT1 subunit of MLCP in the absence or presence of Rho-kinase inhibitor (Y-27632) using aortic tissue from NT and S-P467L mice (n=4–9) and quantification of Y-27632-sensitive Rho-kinase activity. (D–E) Effect of Rho-kinase inhibition (30 min pre-incubation; Y-27632, 1 μmol/L) on contraction or relaxation of aortic rings from S-P467L and NT mice in response to ET-1 (D) or Ach and SNP (E) (n=9–12). (F) Direct blood pressure measurements were recorded in response to acute intravenous injection of the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 in anesthetized NT and S-P467L mice (n=6). See also Figures S1 and S2. * p<0.05 S-P467L vs. NT. # p<0.05 treated vs. non-treated. Error bars represent SEM.