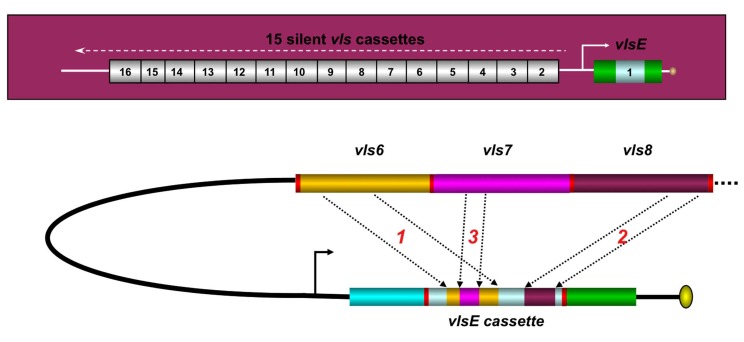
Fig. (3).
The vlsE antigenic variation system of Lyme disease Borrelia. The vls locus of B. burgdorferi B31 (top of figure) consists of the vlsE gene (that encodes the surface lipoprotein VlsE) and a contiguous series of 15 vls silent cassettes (that are not expressed). Each of the silent cassettes are highly homologous to the central cassette region of vlsE, but encode different amino acids in each of 6 variable regions. During mammalian infection, segments of the silent cassettes replace the corresponding region in the vlsE expression site, as shown in the hypothetical example in the lower part of the figure. This process results in vlsE sequence variants that have different amino acid sequences and hence different epitopes. vlsE recombination occurs continuously during mammalian infection, and contributes to immune evasion and long-term survival of Lyme disease Borrelia in humans and other vertebrate hosts. Adapted from Ref. [13].