Figure 5.
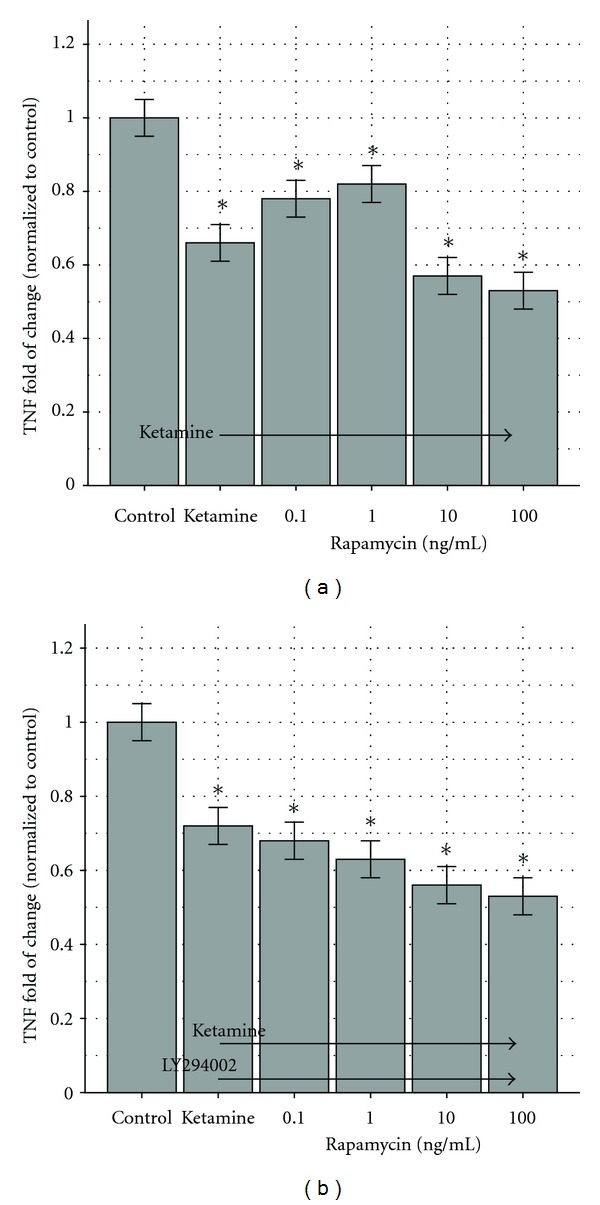
(a) Ketamine and rapamycin modify TNF production by RAW264.7 murine macrophages. LAC wild-type MRSA (USA300) stimulated 34% less TNF secretion by macrophages when exposed to ketamine (second column), and 43% and 47% less than the control (first column) when exposed to a combination of ketamine and rapamycin at 10 ng/mL (fifth column) and 100 ng/mL (sixth column). When ketamine was combined with rapamycin at 0.1 ng/mL (third column) and 1 ng/mL (fourth column), TNF production was suppressed to a lesser extent (22% and 18%, resp.). The suppression observed at 0.1 and 1 ng/mL is different at P < 0.05 than the one observed at 10 and 100 ng/mL, and all concentrations decreased TNF production compared to the control (P < 0.05). The control (first column) is macrophage stimulation without ketamine or rapamycin. The results are depicted as fold of change compared to the control with 95% confidence intervals shown as “error bars.” *P < 0.05. The control response was 29, 229 ± 731 pg/mL. (b) Ketamine, rapamycin, and LY294002 modify TNF production by RAW264.7 murine macrophages. The LAC wild-type MRSA (USA300) strain stimulated less TNF secretion by macrophages when exposed to ketamine, LY294002, and rapamycin. The presence of LY294002 abolished the dose response depicted in Figure 8. Specifically, the reduction with ketamine and LY294002 was 28% (second column). Ketamine plus LY294002 and rapamycin at 0.1 ng/mL (third column) and 1 ng/mL (fourth column) caused reductions of 32% and 37%, respectively. With rapamycin doses of 10 ng/mL (fifth column) and 100 ng/mL (sixth column), the reductions were 44% and 47%. Ketamine with low doses (0.1 and 1 ng/mL) of rapamycin did not give results significantly different from ketamine alone, but higher doses (10 and 100 ng/mL) caused augmented TNF suppression (P < 0.05). The control was macrophage stimulation without ketamine, rapamycin, or LY294002, and the second column shows RAW264.7 cell stimulation in the presence of ketamine only. The results are depicted as fold of change compared to the control with 95% confidence intervals shown as “error bars.” *P < 0.05. The control response was 28, 445 ± 701 pg/mL.
