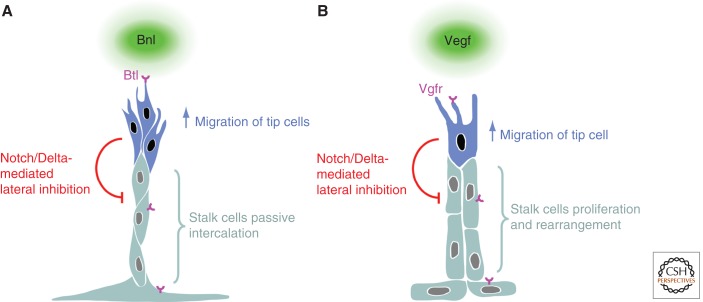
Figure 2.
Branch regionalization and outgrowth. (A) Tracheal branching, and (B) vertebrate angiogenesis. Both Bnl and Vegf ligands elicit a migratory behavior through their respective receptors Btl and Vgfr. In both instances, the cells with the highest receptor activity become tip cells and produce more Delta, leading to the activation of Notch in neighboring stalk cells, which, in turn, inhibit the tip cell fate. Although Fgf signaling in the trachea triggers migration in the tip cells and, as a consequence, passive stalk cell intercalation, Vegf signaling in the vasculature not only triggers tip cell migration but also actively regulates the proliferation and rearrangement of stalk cells.