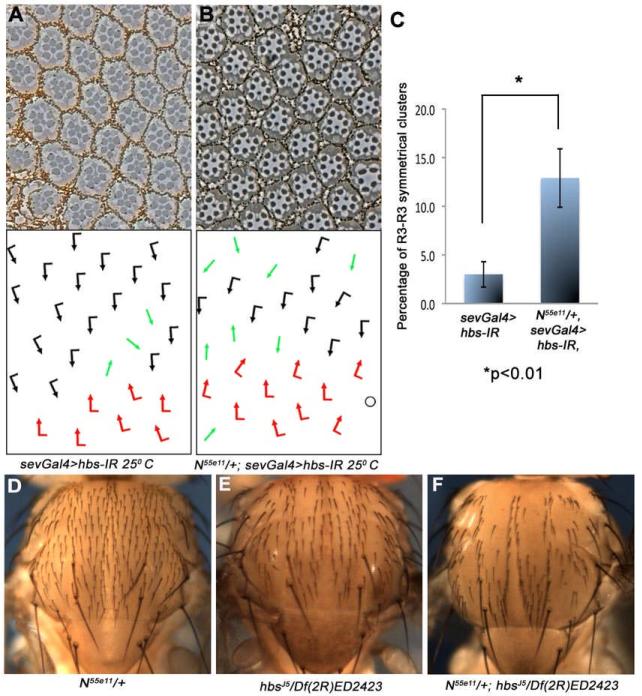
Figure 4. hbs genetically interacts with N.
(A-C) Tangential eye sections of adult eyes of indicated genotypes (at 25°C; centered around the equator); bottom panels show schematic representations of ommatidial polarity. Anterior is left and dorsal is up. (A) sevGal4, UAS-hbs-IR and (B) N-/+; sevGal4, UAS-hbs-IR: The N55e11/+ background enhances the hbs-IR phenotype, most evident in the increase in R3-R3 symmetrical clusters, quantified in (C; graph shows mean standard deviation [s.d.] of three eyes, n>300 ommatidia scored, P-value: *p<0.01 as determined by student t-test).
(D-F) Dorsal thorax view of indicated genotypes, anterior is up. (D) N55e11/+ thorax (control) showing normal sensory bristles arrangement, (E) hbsJ5/Df(2R)ED2423 thorax with some missing bristles, (F) N55e11/+; hbsJ5/Df(2R)ED2423 thorax, note strong enhancement of the hbsJ5/Df(2R)ED2423 phenotype by removing a copy of N.