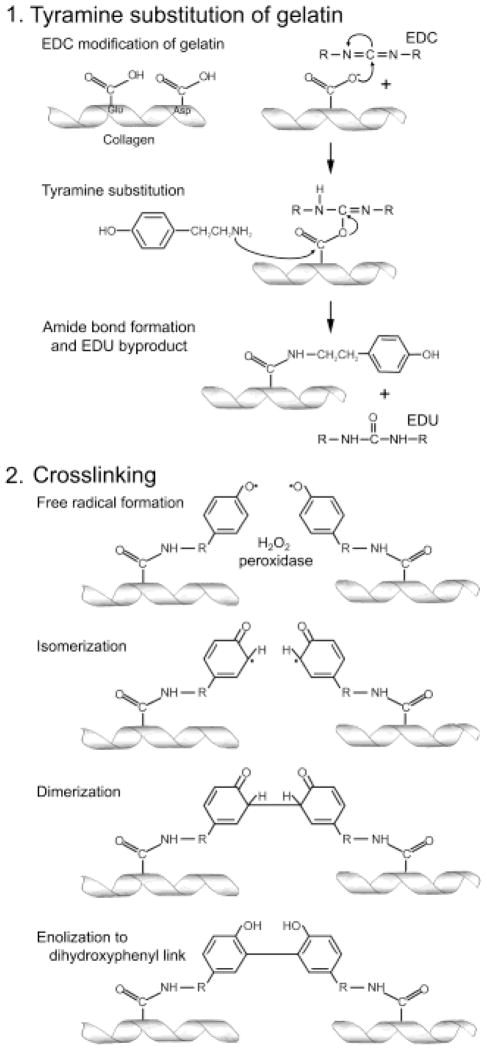
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the two-step process in generating cross-linked T-gelatin.
Step 1: Tyramine addition to gelatin is initiated with EDC modification (to form a reactive O-acylisourea intermediate) of the carboxyl groups on aspartate (Asp) or glutamate (Glu) residues of the individual collagen molecules, followed by substitution of tyramine (nucleophilic attack of the tyramine amine on the carbonyl carbon of the acylisourea intermediate) and displacement of the acylurea form of EDC (EDU). Step 2: Cross-linking reaction is initiated by the addition of peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide that causes an oxidation of tyramine and results in a dihydroxyphenyl link between two collagen chains forming the stable intermolecular cross-link.