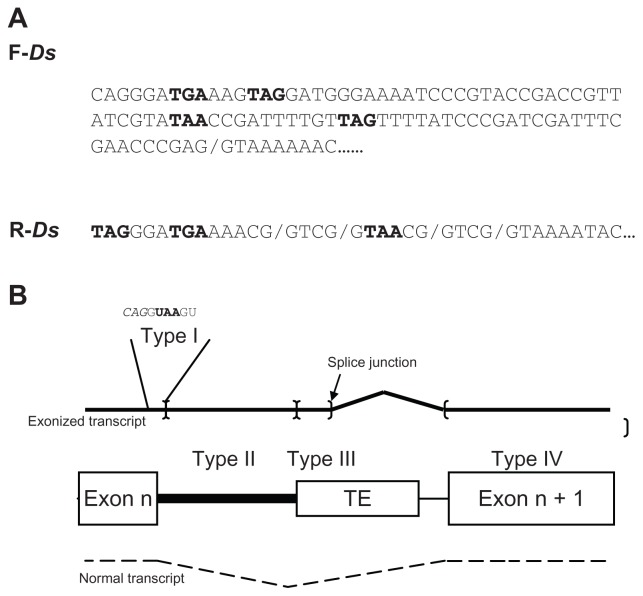
Figure 1.
(A) Ds termini sequences (forward and reverse) providing splice donor junction (slash) and premature termination codons (PTCs) in exonized transcripts (bold). (B) Classification of exonized transcripts (black line) according to location of the PTC.
Notes: Normal transcript is shown as a dashed line. The corresponding DNAs of the TE-inserted target are shown in the center. Black box indicates the unspliced intron. Exonization occurs by using the splice donor (arrow) of TE to join the upcoming exon. The existence and location of an in-frame PTC determines the type of the exonized transcripts, classified into 5 types. As an example, for type I, a PTC (UAA in bold) locates in the skipped exon/intron consensus: italics indicate exonic sequences. Brackets indicate the boundaries of PTC location for classification. Type V transcripts have no in-frame PTC until the end of the gene.