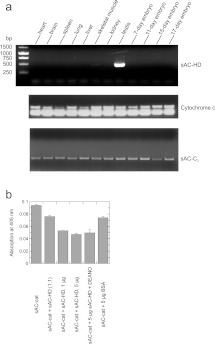
Figure 5. Tissue-specific expression of sAC-HD and effect of sAC-HD on the activity of the sAC catalytic domains.
(A) The agarose gel shows products of PCR with primer pairs specific for sAC-HD, the sAC-C2 domain and for cytochrome c as a control, respectively, applied to a panel of mouse tissue cDNA samples as templates. The sAC catalytic domain C2 could be detected in all tissues, but cDNA coding for sAC-HD was significantly amplified only from skeletal muscle and testis cDNA. (B) In a competitive cAMP formation assay (increasing activity leads to decreasing signals), addition of sAC-HD leads to a concentration-dependent increase of the activity of the catalytic domains. BSA addition served as a control. Adding NO together with the sAC-HD did not modulate the activating effect of sAC-HD. Data represent averages of duplicates and are shown as signals relative to control, and error bars represent relative percentage differences.