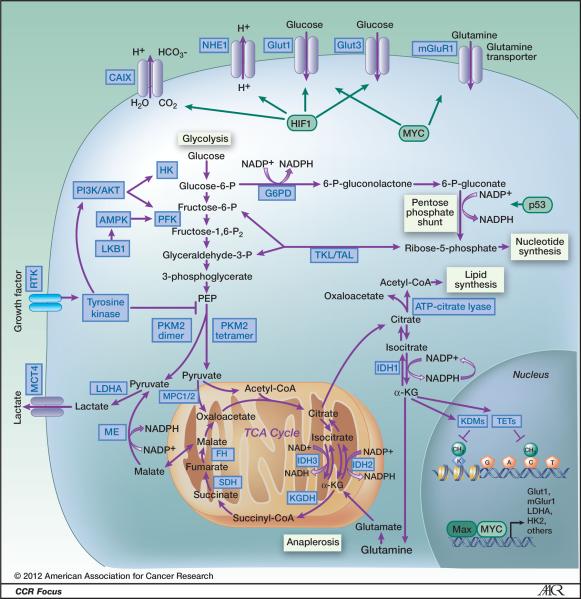
Figure 2.
Schematic illustrating metabolic pathways prominent in malignant cells. Blue boxes indicate enzymes and transporters that may be useful therapeutic targets in cancer. Green boxes represent transcription factors that alter metabolic pathways. Glycolysis is the ten-step metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP and NADH. The pentose phosphate pathway is a process that generates NADPH and 5-carbon sugars as alternative to glycolysis. Nucleotide synthesis provides molecules that make up the individual structural units of the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cell signaling (cGMP and cAMP), are cofactors of enzymatic reactions, and nucleoside triphosphates are sources of chemical energy. Fatty acid synthesis is the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors via fatty acid synthases. Anaplerotic reactions are those that replenish and maintain intermediates of a metabolic pathway. The abbreviations are: CAIX, Carbonic anhydrase IX; NHE1, Na+/H+ exchanger; Glut1, glucose transporter 1; Glut3, Glucose transporter 3; mGluR1, metabotropic glutamate receptor 1; PI3K/AKT, phophotidylinositol-3-kinase/Protein kinase B; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; LKB1, serine/threonine kinase 11 (STK11), liver kinase B1; TKL/TAL, transketolase-transaldolase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; PKM2, pyruvate kinase M2; MCT4, monocarboxylate transporter 4; IDH1 isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; IDH2, isocitrate dehydrogenase 2; IDH3, isocitrate dehydrogenase 3; LDH-A, lactate dehydrogenase A; MPC1/2, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1/2; ME, malic enzyme, malate dehydrogenase; FH, fumarate hydratase; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; KGDH, 2-keto-glutarate dehydrogenase; TETs, DNA hydroxylases; KDMs, lysine histone demethylases; HK, hexokinase; HIF1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; TCA cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle.