Table 2.
Cognitive ability at the ages of 20.1 and 68.5 years in the offspring who were born after normotensive pregnancies (n = 252) and pregnancies complicated by hypertensive disorders (n = 146)
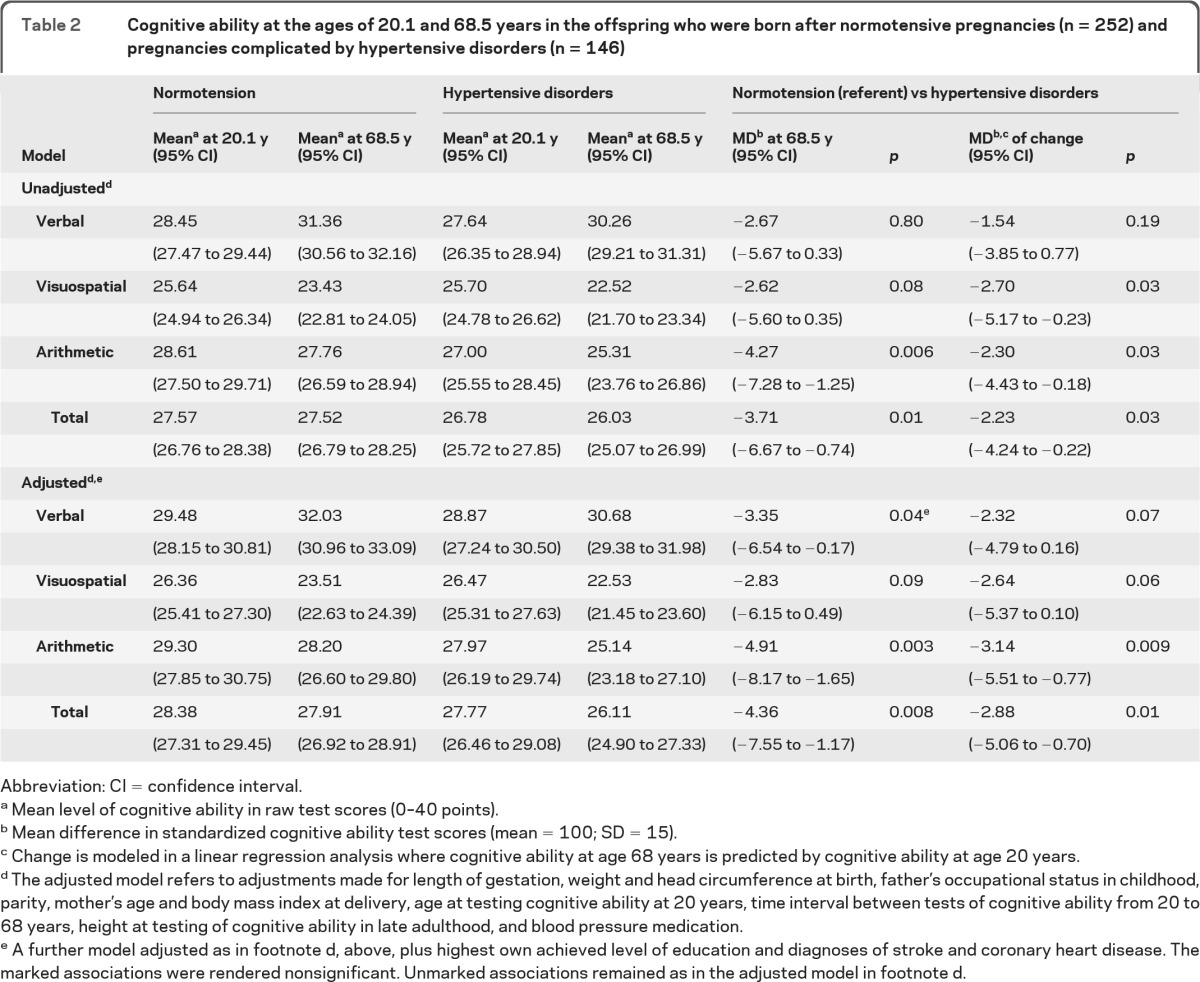
Abbreviation: CI = confidence interval.
Mean level of cognitive ability in raw test scores (0–40 points).
Mean difference in standardized cognitive ability test scores (mean = 100; SD = 15).
Change is modeled in a linear regression analysis where cognitive ability at age 68 years is predicted by cognitive ability at age 20 years.
The adjusted model refers to adjustments made for length of gestation, weight and head circumference at birth, father's occupational status in childhood, parity, mother's age and body mass index at delivery, age at testing cognitive ability at 20 years, time interval between tests of cognitive ability from 20 to 68 years, height at testing of cognitive ability in late adulthood, and blood pressure medication.
A further model adjusted as in footnote d, above, plus highest own achieved level of education and diagnoses of stroke and coronary heart disease. The marked associations were rendered nonsignificant. Unmarked associations remained as in the adjusted model in footnote d.
