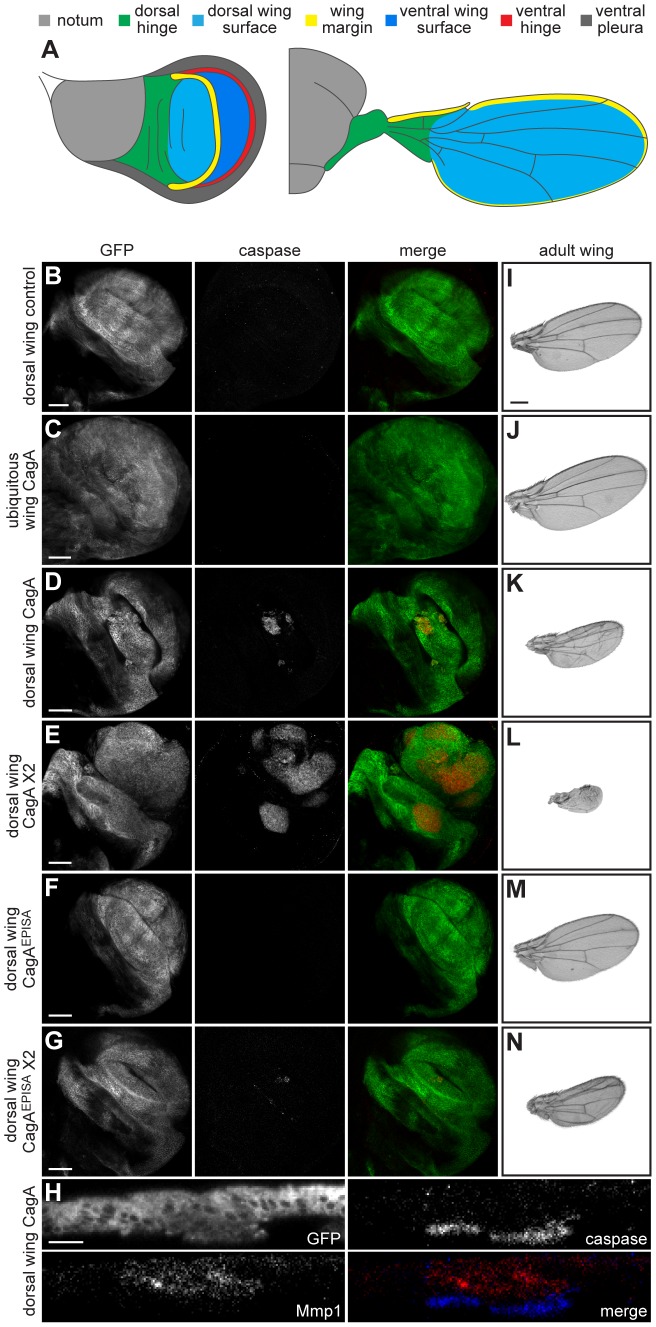
Figure 1. CagA expression causes apoptosis and epithelial disruption.
(A) Schematic illustrating the fate of different domains within the wing imaginal disc. Each color-coded region of the larval structure on the left corresponds to the specified region of the adult wing on the right (modified from [24]). (B–G) Confocal cross sections of male third instar larval wing imaginal discs showing mGFP expression and stained with an antibody against active caspase-3 to mark apoptotic cells. A control wing disc epithelium expressing only mGFP with the bx-GAL4 dorsal wing driver (B) lacks apoptotic cells. Ubiquitous expression of CagA in the wing disc with the 765-GAL4 driver (C) does not cause apoptosis, while expressing CagA with bx-GAL4 (D) triggers formation of apoptotic clusters within the expression domain. Expressing two copies of CagA with bx-GAL4 (E) causes a dose-dependent enhancement of the apoptosis phenotype. Expressing CagAEPISA with bx-GAL4 (F) does not cause a phenotype, while expressing two copies of CagAEPISA (G) produces small apoptotic clusters. Scale bars, 50 µm. (H) XZ confocal plane of a male wing imaginal disc epithelium expressing mGFP and CagA with bx-GAL4 stained with antibodies against active caspase-3 to show basal extrusion of apoptotic cells and matrix metalloproteinase 1 (Mmp1) to show evidence of basement membrane breakdown. Scale bar, 20 µm. (I–N) Adult wing images from male flies of each indicated genotype. Neither expression of mGFP alone with bx-GAL4 (I) nor expression of CagA with 765-GAL4 (J) causes a phenotype in the adult wing. Dorsal wing expression of CagA with bx-GAL4 (K) disrupts epithelial integrity in a dose-dependent manner (L). Expressing CagAEPISA with bx-GAL4 (M) does not cause an adult wing phenotype, while expressing two copies of CagAEPISA (N) causes epithelial disruption. Scale bar, 500 µm.