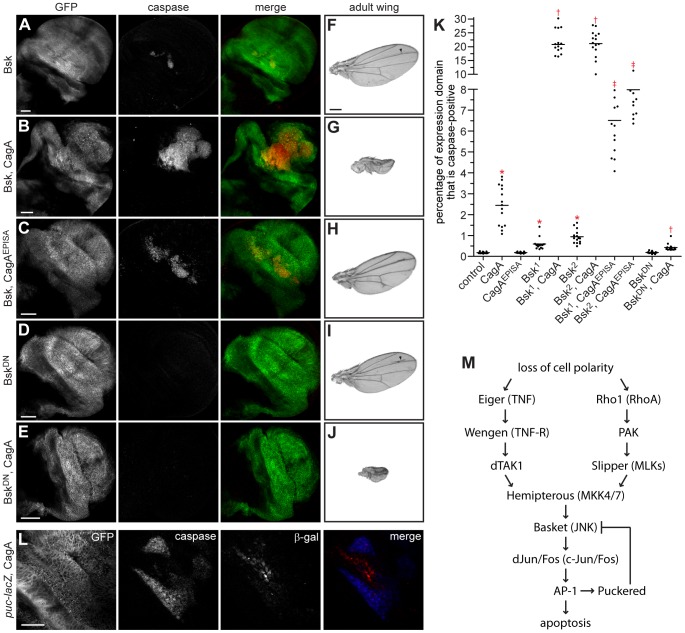
Figure 2. CagA-induced apoptosis occurs through JNK pathway activation.
(A–E) Confocal cross sections of male third instar larval wing imaginal discs showing mGFP expression with bx-GAL4 and stained with an anti-active caspase-3 antibody to mark apoptotic cells. Ectopic overexpression of wild type Bsk in the dorsal wing disc (A) causes a mild apoptosis phenotype that is strongly enhanced by coexpression with CagA (B). Coexpression of Bsk with CagAEPISA (C) also enhances the apoptosis phenotype. Expression of BskDN alone (D) does not cause apoptosis, and coexpression with CagA (E) strongly suppresses apoptosis induced by CagA expression. Scale bars, 50 µm. (F–J) Adult wing images from male flies expressing different forms of Bsk alone or in combination with CagA. Ectopic overexpression of Bsk with bx-GAL4 (F) causes only subtle vein defects in the adult wing, while coexpression with CagA (G) enhances epithelial disruption. Coexpression of Bsk with CagAEPISA (H) does not significantly affect formation of the adult wing structure. Expression of BskDN with bx-GAL4 (I) also causes only subtle vein defects in the adult wing, while coexpression with CagA (J) enhances epithelial disruption. Arrowheads highlight ectopic veins in adult wings expressing different forms of Bsk alone. Scale bar, 500 µm. (K) Quantitation of apoptosis as a percentage of the expression domain showing active caspase-3 staining, n = 15 wing discs per genotype; bar indicates average value for each group. * indicates values that differ significantly from the control with expression of a single transgene; † indicates values that show significant enhancement or suppression compared to CagA; ‡ indicates values that show significant enhancement compared to CagAEPISA; p<0.0001. (L) Confocal cross section of a male wing imaginal disc epithelium carrying the puc-lacZ reporter allele and expressing mGFP and CagA with bx-GAL4. Staining with antibodies against active caspase-3 and β-galactosidase (β-gal) shows that apoptotic cells lie adjacent to those in which JNK signaling has been activated. Scale bar, 50 µm. (M) A model of the JNK pathway depicting the multiple upstream activators known to induce JNK-dependent apoptosis in Drosophila, and indicating human homologs for each pathway component.