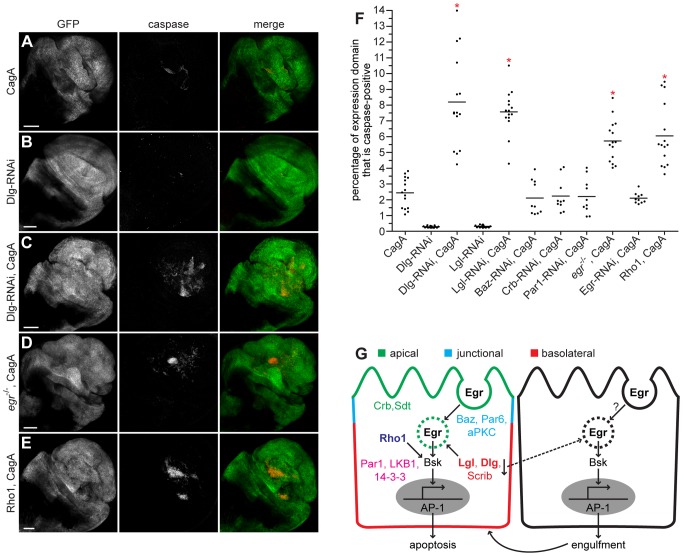
Figure 3. CagA genetically interacts with nTSGs, Eiger and Rho1.
(A–E) Confocal cross sections of male third instar larval wing imaginal discs showing mGFP expression with bx-GAL4 and stained with anti-active caspase-3 antibody to mark apoptotic cells. Dorsal wing expression of CagA with bx-GAL4 (A) causes formation of apoptotic clusters. RNAi-mediated knockdown of the nTSG Dlg alone (B) does not cause significant apoptosis, but enhances apoptosis induced by CagA expression (C). The apoptosis phenotype is enhanced when CagA is expressed in an egr mutant background (D). Coexpression of Rho1 with CagA (E) also enhances apoptosis. Scale bars, 50 µm. (F) Quantitation of apoptosis as a percentage of the expression domain showing active caspase-3 staining, n = 10 or 15 wing discs per genotype; bar indicates average value for each group. * indicates values that show significant enhancement compared to CagA, whose quantitation (from Figure 2) is provided for comparison; p<0.0001. (G) A model showing the localization of polarity protein complexes in an epithelial cell, their known interactions with other upstream activators of JNK signaling in Drosophila, and the downstream effects of these interactions.