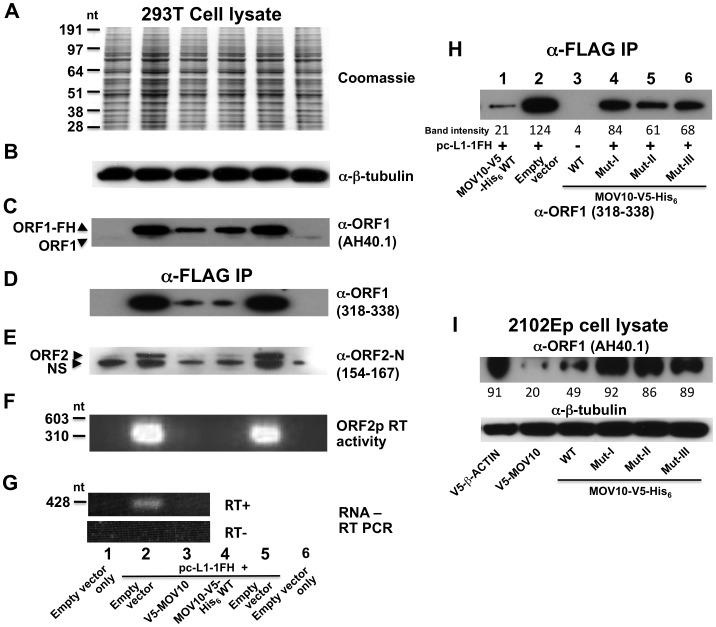
Figure 5. MOV10 inhibits exogenous L1 RNP expression in cells.
(A–C) Analysis of 293T cell lysates showing that MOV10 expression has no discernable effect on total protein production as determined by (A) Coomassie blue staining, or (B) Western blot detection of constitutively expressed proteins. (C) However, MOV10 attenuates expression of ORF1p from pc-L1-1FH. Note, α-ORF1 AH40.1 only faintly detects endogenous ORF1 protein in this blot exposure. (D–G) Analysis of immunoprecipitate samples following IP of pc-L1-1FH. Levels of (D) ORF1p, (E) ORF2p, (F) ORF2p RT activity, and (G) L1 RNA are strongly diminished in the presence of MOV10. α-ORF2-N occasionally detects a slightly smaller than expected band in untransfected cells (labeled NS in (E)). It is not known if this band is non-specific or a truncated form of endogenous ORF2p. Lane names and numbers at the bottom refer to all panels A–G. (H) Analysis of 293T immunoprecipitate samples following α-FLAG IP of cotransfected pc-L1-1FH. Introducing mutations in helicase domains of MOV10 significantly abrogates its inhibition of ORF1p expression from pc-L1-1FH (compare also with panel D). (I) V5-MOV10 protein was expressed in 2102Ep cells, and endogenous ORF1 protein was detected in lysates with α-ORF1 AH40.1 antibody. Endogenous ORF1p levels decrease in the presence of MOV10 wild-type protein, but to lesser degree with MOV10 mutants (lower panel, lanes 4–6). ImageJ software (NIH) was used to quantitate band intensities, and their absolute readings are arrayed below the figure panels (H and I).