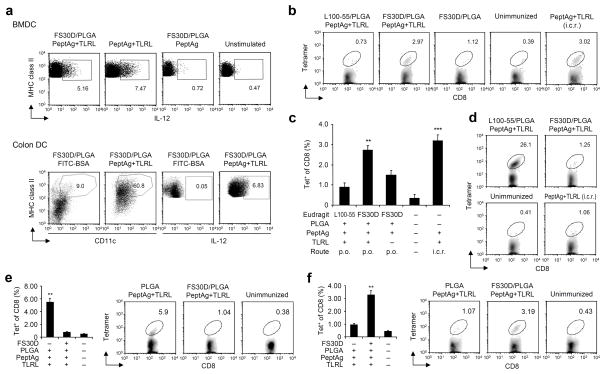
Figure 2.
Orally delivered FS30D-coated PLGA nanoparticle vaccine induces antigen-specific T cells in the large intestine, while L100-55-coated vaccine induces the T cells in the small intestine. (a) Activation of DC after 20-h incubation with supernatants from FS30D-coated PLGA containing PCLUS3-18IIIB+TLRL (FS30D/PLGA/PeptAg+TLRL), antigen (FS30D/PLGA/PeptAg) or vaccine only (PeptAg+TLRL) dissolved in PBS at pH 7.4 for 16 h (upper panels). Intracellular IL-12 was measured by flow cytometry (n = 6 per group). The micro/nanoparticles were also given orally and DC activation in vivo was assessed ex vivo (lower panels), n = 5 per group. (b–d) Induction of T cell responses after oral delivery of FS30D/PLGA/PeptAg+TLRL or L100-55/PLGA/PeptAg+TLRL. Oral administration was conducted twice with a two-week interval. Tetramer positive cells in the colorectum (b and c) or upper part of the small intestine (d) were measured three weeks after. The i.c.r. group was immunized with vaccine only without nanoparticles but formulated in DOTAP. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 indicate the significant difference between the group with asterisks and each of the groups without asterisks. There are no differences between the two groups with asterisks. Representative of experiments (c) is summarized in b. In d, P < 0.001 for L100-55 vs other groups. n = 8 12 per group. (e and f) T cell responses induced after oral delivery of uncoated or FS30D-coated PLGA/PeptAg+TLRL. Tetramer positive cells in the upper small intestine (e) or the colorectum (f) were measured. **P < 0.01 indicates the significant difference between groups (n = 7 per group).