Figure 5. DISC1 mutant mice exhibit greater responses to an NMDA antagonist, MK-801, and D-serine treatment.
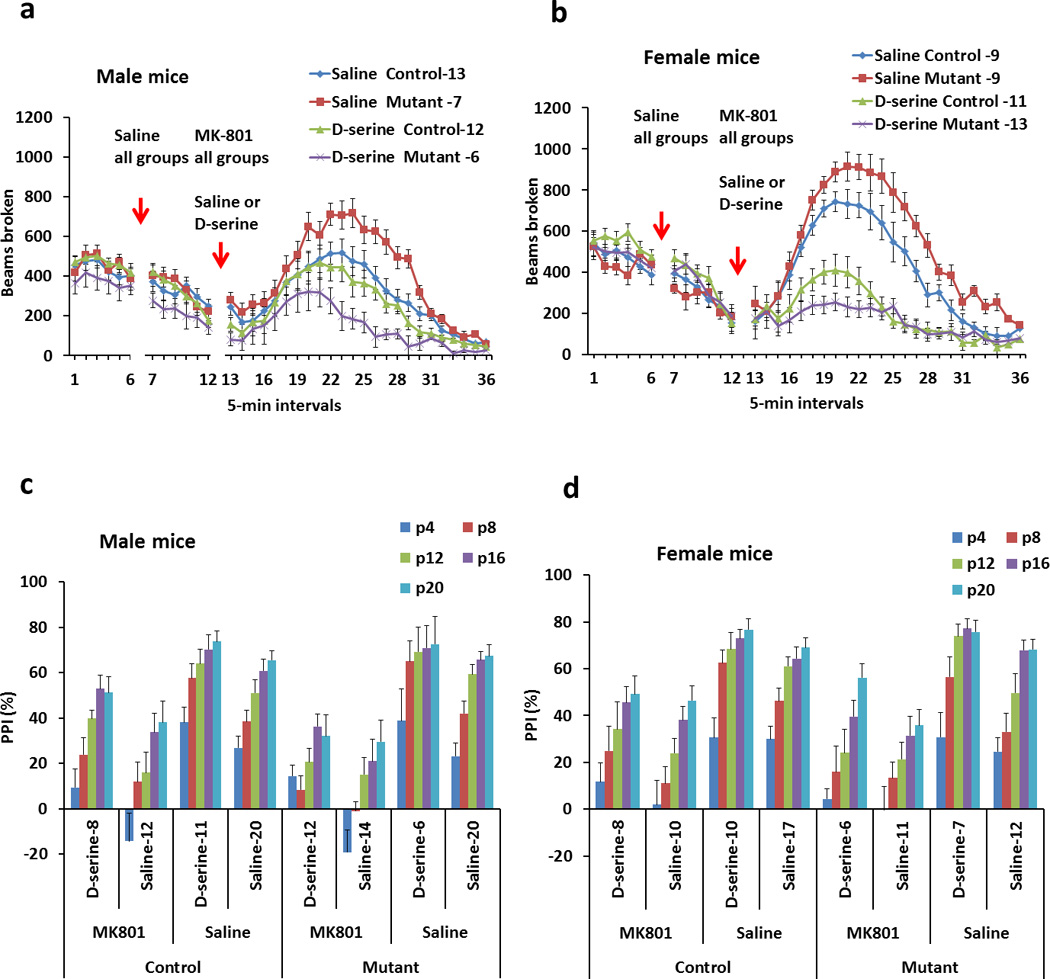
[a] Locomotor activity in open field of male mice before and after treatment with MK-801 (0.3 mg/kg, i.p.) followed by saline or D-serine injections (2.7 g/kg, i.p.). Compared to control male mice, mutant male mice display significantly greater activity in response to MK-801. Compared to control male mice, mutant mice also exhibit significantly greater sensitivity to the ameliorative effects of D-serine. Numbers of mice in each group are indicated on the graph.
[b] Locomotor activity in open field of female mice before and after treatments with MK-801 (0.3 mg/kg, i.p.) followed by saline or D-serine injections (2.7 g/kg, i.p.). Compared to control female mice, mutant female mice exhibit significantly higher locomotor activity in response to MK-801. Compared to control female mice, mutant female mice show significantly greater sensitivity to the ameliorative effects of D-serine. Numbers of mice in each group are indicated on the graph.
[c] PPI of the acoustic startle of male mice before and after treatment with MK-801 (0.3 mg/kg, i.p.) followed by saline or D-serine injections (2.7 g/kg, i.p.). p4–20 are the intensities of pre-pulses above the background noise level (70dB). Compared to control male mice, mutant male mice display greater MK-801 induced impairment in PPI at P4 and P8. Compared to control male mice, mutant mice also exhibit significantly greater sensitivity to the ameliorative effects of D-serine at P4. Numbers of mice in each group are indicated on the graph.
[d] PPI of the acoustic startle of female mice before and after treatment with MK-801 (0.3 mg/kg, i.p.) followed by saline or D-serine injections (2.7 g/kg, i.p.). Numbers of mice in each group are indicated on the graph.
