Figure 1.
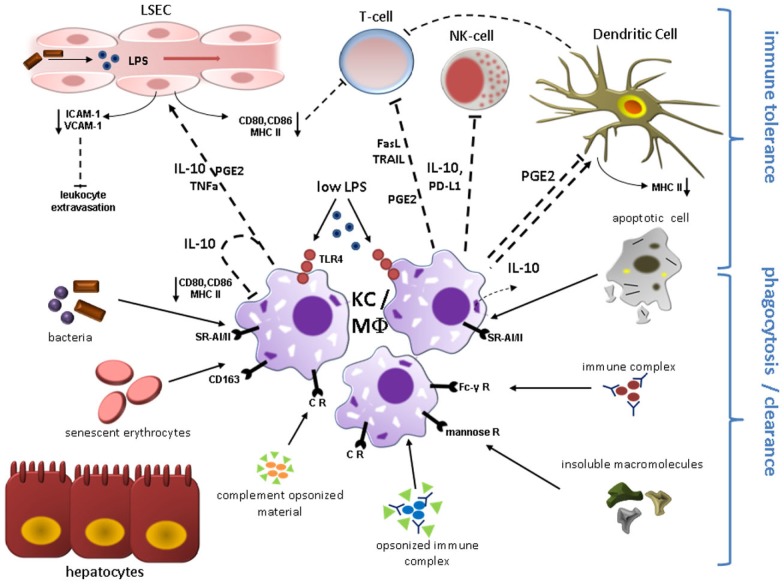
Kupffer cell (KC)/Macrophage (MΦ) function during liver homeostasis. Phagocytosis and induction of immune tolerance as the two main functions of KCs/hepatic MΦ in the steady state are depicted here. KCs reside in the liver sinusoids in close proximity to sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSEC) and immune cells entering the liver microvasculature mainly through the portal vein. KCs express a broad range of surface receptors mediating phagocytosis, which renders these cells as highly effective filters of endogenous and exogenous antigens. Complement receptors mediate removal of complement-opsonized material. Circulating non-opsonized immune globulin complexes are cleared through Fc-γ Receptors. Insoluble macromolecules from multiple sources are effectively cleared after binding to Scavenger Receptors including CD163 for senescent erythrocytes. Molecules with a mannosyl motif are phagocytized following engagement of mannose receptors. Engulfment of apoptotic cell constituents can induce secretion of immunosuppressive IL-10 which likely contributes to the immune modulatory function of quiescent KCs. Constant exposure to gut-derived LPS via TLR4 also results in expression of IL-10 and PGE2 that can directly inhibit T-cell and NK-cell function and mediate down-regulation of co-stimulatory proteins including CD80, CD86, and MHC class II on endothelial cells, dendritic cells, and KCs constituting liver APCs, which further attenuates T-cell activation. KC-secreted PD-L1 and release of apoptosis-inducing mediators (TRAIL, FasL) contribute to suppression of adaptive and innate immune response through inactivation/elimination of T-cells and NK-cells. IL-10, PGE2, and TNF-alpha lead to reduced expression of adhesion molecules (VCAM-1; ICAM-1) on LSEC, thereby limiting leukocyte influx. Abbreviations: APC, antigen presenting cell; CR, complement receptor; FasL, Fas ligand; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; PD-L, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; SR-AI/II, scavenger receptor AI/AII; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand; VCAM-1, vascular adhesion molecular 1.