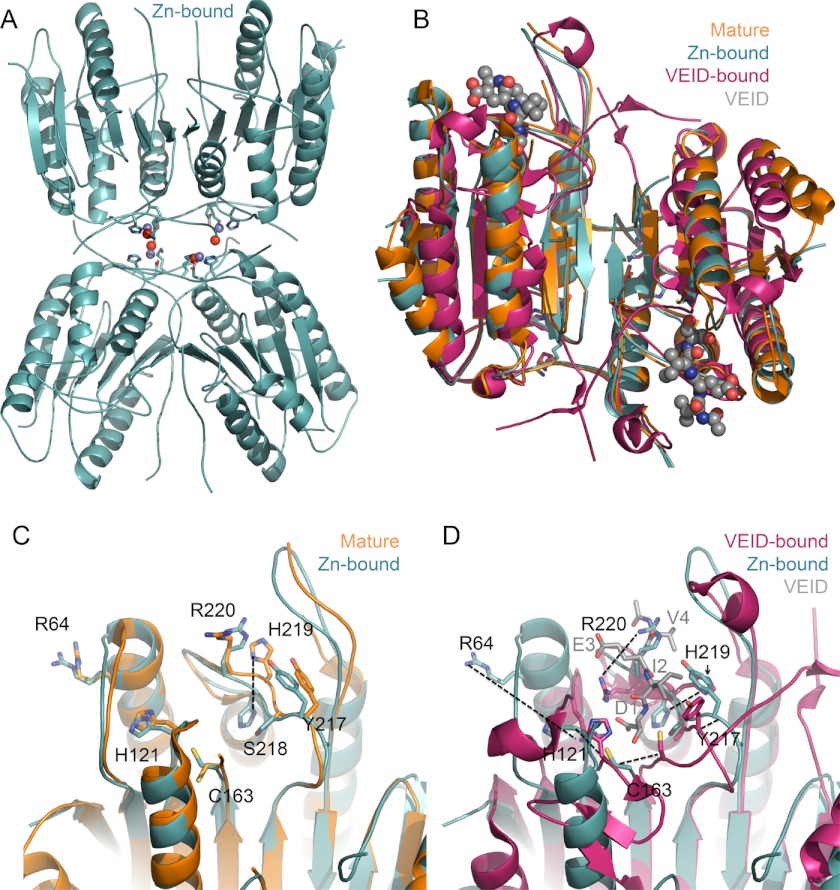
FIGURE 3.
Zinc-bound caspase-6 retains fold. A, zinc-bound caspase-6 retains the same fold as zinc-free caspase-6, with one zinc bound per monomer. The zinc (blue sphere), zinc ligands Lys-36, Glu-244, and His-287 (sticks), and a water (red sphere) are shown. B, superposition of available caspase-6 structures underscores that zinc does not change the overall fold in caspase-6. Zinc-bound caspase-6 (4FXO, light blue) is in the helical conformation seen in unliganded, mature caspase-6 (3K7E, orange), which differs from VEID-bound (3OD5, red) caspase-6. The substrate VEID (gray spheres) indicates the substrate-binding region. Only in mature caspase-6 and the zinc-bound form of caspase-6 are the extended helical state of the 60s and 130s helices observed. C, superposition of caspase-6 active site in the apo, mature (3K7E, orange), and zinc-bound (4FXO, light blue) structures. Of the residues in this region, only His-219 undergoes a significant shift in conformation. D, superposition of VEID-bound (3OD5, red) and zinc-bound (4FXO, light blue) caspase-6 highlights the significant conformational change that caspase-6 undergoes during conversion from the helical to canonical structures. The substrate-mimic VEID (gray) is labeled as D1, I2, E3, and V4 to indicate the peptide subsite positions within the peptide.