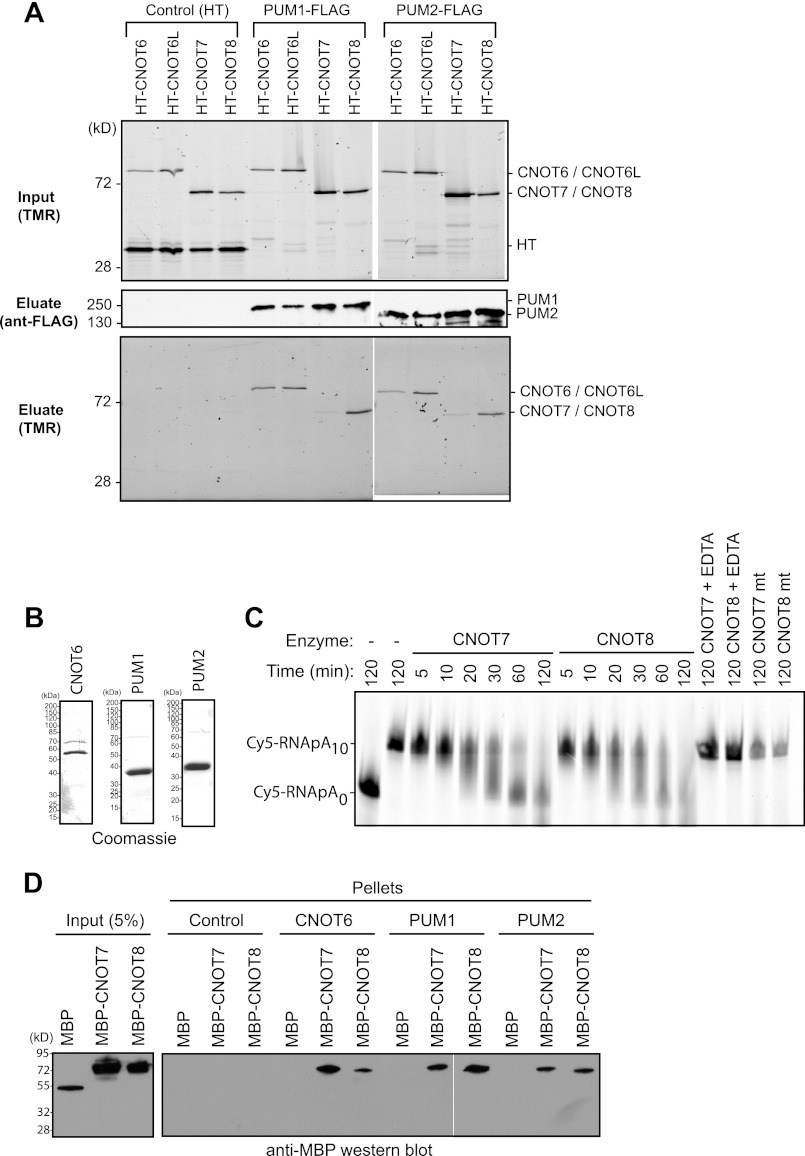
FIGURE 4.
PUM1 and PUM2 interact with deadenylase subunits of the CNOT complex. A, deadenylases, fused to Halotag, coimmunoprecipitate (Eluate) with FLAG-tagged PUM1 and PUM2 from RNase-treated extracts (Input). As a negative control (Control), mock immunoprecipitations were performed with anti-FLAG beads from samples expressing Halotag (HT) protein and Halotag deadenylase fusion proteins. Proteins were detected in input extracts or purified FLAG eluates by fluorescence labeling with the Halotag ligand TMR or by anti-FLAG Western blot. B, Coomassie staining of recombinant, purified bait proteins: CNOT6, PUM1, and PUM2. PUMs were active for RNA binding (Fig. 1B). C, in vitro deadenylation assay using wild-type CNOT7 and CNOT8 or mutant CNOT7 mt and CNOT8 mt with Cy5-labeled RNA substrate with a 10-nucleotide poly(A) tail (Cy5-RNApA10) or, as a marker, substrate lacking a tail (Cy5-RNApA0). EDTA was added as a negative control to chelate Mg2+ and thus inhibit deadenylation. D, Western blot (anti-MBP) of in vitro binding of recombinant, purified PUM1 and PUM2 to CNOT7 and CNOT8. Halolink bound PUM1 and PUM2 were incubated with MBP fusions of CNOT7 or CNOT8. As a positive control, CNOT7 and CNOT8 interacted with CNOT6. Halolink beads alone (Control) and MBP served as negative controls.