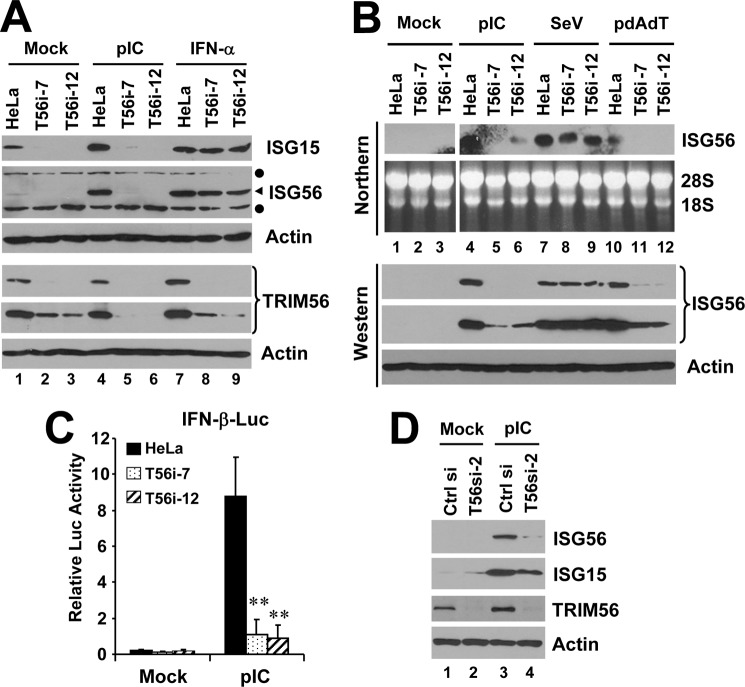
FIGURE 3.
Effects of TRIM56 knockdown on IFN induction and ISG expression in HeLa cells following various stimuli. A, control HeLa and HeLa cells with stable knockdown of TRIM56 (T56i-7 and T56i-12) were mock-treated, stimulated with poly-I:C or IFN-α for 12 h. Cells were lysed for immunoblotting of ISG15, ISG56, TRIM56 (two different exposures of the blot are shown) and actin expression. Filled circles denote nonspecific bands. B, control HeLa, HeLa T56i-7 and T56i-12 cells were mock-treated, stimulated with poly-I:C, infected with SeV, or transfected with poly-dA:dT for 12 h. Northern blotting was performed to quantify the expression of ISG56 transcript. The ethidium bromide-stained 18S and 28S rRNAs served as loading controls (upper panel). Western blotting (lower panel) was carried out to determine the expression levels of ISG56 protein (two different exposures of the blot are shown). Actin was blotted to demonstrate equal sample loading. C, IFN-β promoter activities in control HeLa, HeLa T56i-7, and T56i-12 cells mock-stimulated or stimulated by poly-I:C for 8 h. ** indicates statistical difference exists with a p value of <0.01 when compared with HeLa cells stimulated by poly-I:C. D, HeLa cells were transiently transfected with a scrambled control siRNA or TRIM56 siRNA#2. 48 h later, cells were mock-treated or stimulated by poly-I:C for 12 h, followed by cell lysis and immunoblotting of ISG56, ISG15, TRIM56, and actin expression. Note that poly-I:C moderately up-regulated TRIM56 expression in cells transfected with control siRNA (compare lanes 3 versus 1).